Modulation
Modulator Lane
Modulators
Envelope
LFO
LFO Table
Curve
Random
Audio Follower
Pitch Tracker
Note
Pressure
Velocity
Pitch Wheel
Note Gate
MIDI CC
MPE Timbre
Remap
Lower Limit / Upper Limit
Scale
Sample & Hold
Triggering
Overview

 Almost all parameters in the Kilohearts Ecosystem can be modulated. Modulators can be added as modules in the horizontal lane along the bottom of the screen. The macro buttons at the top of the screen also use the modulation system and are hooked up to their targets in the same way as other modulators like envelopes and LFOs.
Almost all parameters in the Kilohearts Ecosystem can be modulated. Modulators can be added as modules in the horizontal lane along the bottom of the screen. The macro buttons at the top of the screen also use the modulation system and are hooked up to their targets in the same way as other modulators like envelopes and LFOs.
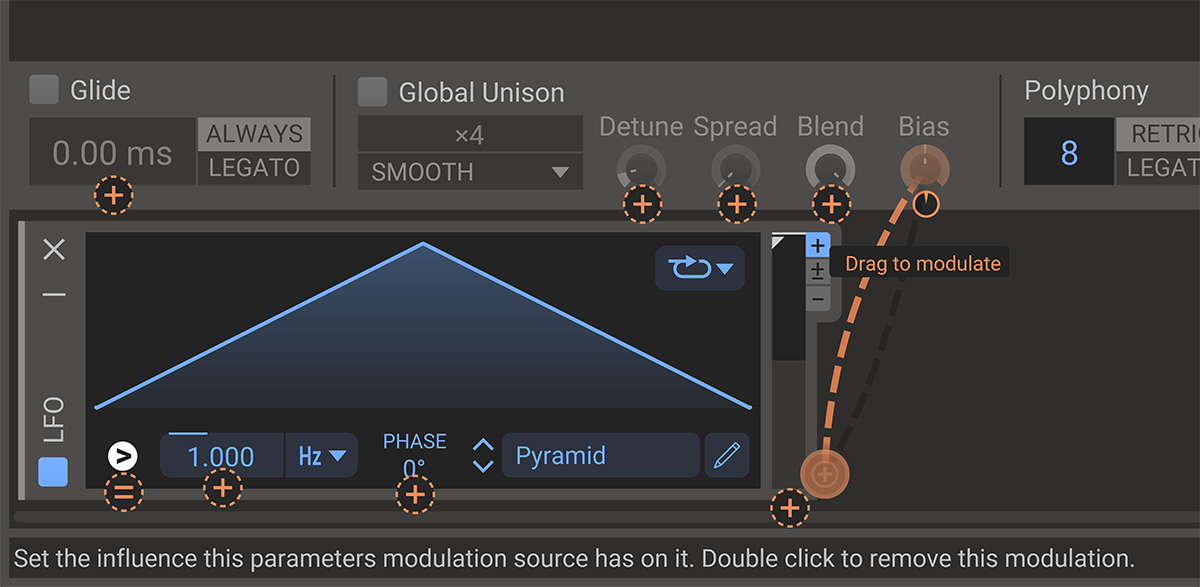
Hooking up a modulation source to a target parameter is done in pretty much the same way for all modulation sources. Look for the little plus icon appearing when you are hovering your mouse pointer over a modulation source. Clicking the plus icon selects the modulation source and switches the UI over to modulation target selection mode. In this mode, a small orange modulation knob will appear next to each possible modulation target. Click and drag on the modulation knob to connect the modulation source to the target parameter and set the modulation level. The modulated control will turn to an orange color to indicate that it is being modulated.
After a modulation source has been connected to a target parameter, the modulation knob will be visible next to the modulation source at all times. The modulation knob will also appear next to the modulation target when the target is hovered. The modulation knob can be dragged to adjust the level of modulation. To disconnect the modulation, double click the modulation knob.
To better understand the modulation system it is useful to understand some of the internal timing of Phase Plant. Values in the generator section are updated for every sample. This is called "at audio rate". While modulators output values much less often. Typically every 64 samples, but it can be more often depending on your DAW settings and other circumstances. We call this "at control rate". Therefor there is a limit on how fast the output of your modulators can change. Anything around 100 Hz or higher is likely so affected by aliasing that it it impossible to make any controlled changes to it. It's mostly just static. If you want very fast modulations, consider using the audio rate modulation system available in the generator stack only.
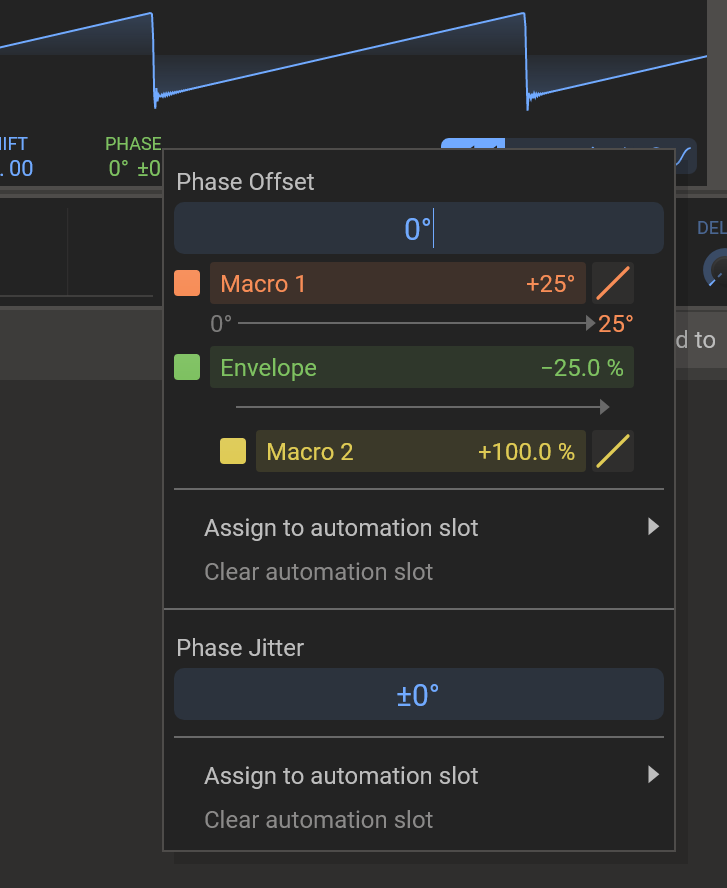 Modulations are color coded. Control rate modulations are shown in orange in the UI, audio rate modulations are shown in green, and modulations scaling other modulations are shown in yellow. Right-clicking any control will show you a context menu for it. This menu also holds some more detailed descriptions of any modulations that may affect it. In the example imaged we see the Phase parameter of an Analog generator being modulated by two sources, and a third source used to modulate the amount of modulation for the audio rate modulation. Each row represents one modulation. The very left square of color on each row is a toggle to temporarily disable their respective modulation. Then follows the name of the modulation source, and the modulation amount. To the right is a diagonal line that describes the "curvature" of each modulation, and is similar to using a Remap modulator. It can be bent upwards or downwards to create non-linear modulation results. Even further right an "x" button will appear if you hover each row, to delete the modulation. Under each row an arrow is displayed showing the upper and lower bounds of the results of the modulation on the original parameter. You can set these bounds instead of the modulation amount if you need that sort of precision. Bear in mind that these bounds can only be shown for one modulation each, and the total of all modulations may lead to values outside the bounds of each individual modulation.
Modulations are color coded. Control rate modulations are shown in orange in the UI, audio rate modulations are shown in green, and modulations scaling other modulations are shown in yellow. Right-clicking any control will show you a context menu for it. This menu also holds some more detailed descriptions of any modulations that may affect it. In the example imaged we see the Phase parameter of an Analog generator being modulated by two sources, and a third source used to modulate the amount of modulation for the audio rate modulation. Each row represents one modulation. The very left square of color on each row is a toggle to temporarily disable their respective modulation. Then follows the name of the modulation source, and the modulation amount. To the right is a diagonal line that describes the "curvature" of each modulation, and is similar to using a Remap modulator. It can be bent upwards or downwards to create non-linear modulation results. Even further right an "x" button will appear if you hover each row, to delete the modulation. Under each row an arrow is displayed showing the upper and lower bounds of the results of the modulation on the original parameter. You can set these bounds instead of the modulation amount if you need that sort of precision. Bear in mind that these bounds can only be shown for one modulation each, and the total of all modulations may lead to values outside the bounds of each individual modulation.
Modulator Lane
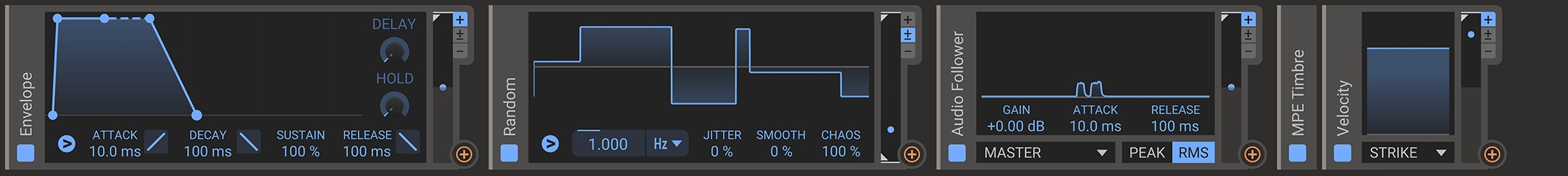
Along the bottom of the screen is the modulator lane. Here you can add modules that can be used for modulation such as LFOs and envelopes. It's possible to add up to 32 modulator modules. To add a modulator, click on the icon that appears in the lane as you hover it (the dotted area).
All modulator modules have a small animated display at the right hand side that shows the current value that the modulator outputs. The value for the most recent voice is shown in blue, and the other voices are drawn in grey. Some modulators also have a global value which is used when modulating parameters which are not tied to a voice. This is also displayed in grey.
The output depth of all modulators can be scaled by clicking and dragging on the animated output display. The depth can also be modulated by routing another modulation to this parameter.
To the right in most modulator modules, you can change its output range. The available options are unipolar (+, output ranging from 0 to 1), bipolar (+/-, output ranging from -1 to +1) and inverted (-, output is same as unipolar only inverted going from minimum 1 "up to" 0.).
Modulators
Envelope
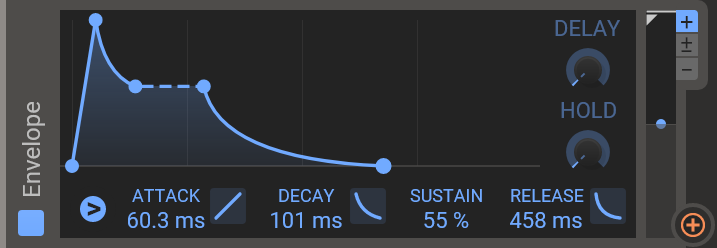 The envelope modulator is a modulator module that provides an envelope that you can use as a modulation source.
The envelope modulator is a modulator module that provides an envelope that you can use as a modulation source.
It uses a standard Kilohearts envelope, and the modulation triggering functionality is described in detail in the triggering chapter.
- Trigger
- This is meant as a modulation target for remotely triggering the Envelope to restart. Right-clicking on the trigger button will bring up the triggering menu. The modulation triggering functionality is described in detail in the triggering chapter.
The Envelope Modulator has one additional setting in the menu, Seamless. When enabled, the envelope will restart from the current value when triggered, instead of resetting the envelope to zero (i.e. the attack will start in the middle of the release).
LFO
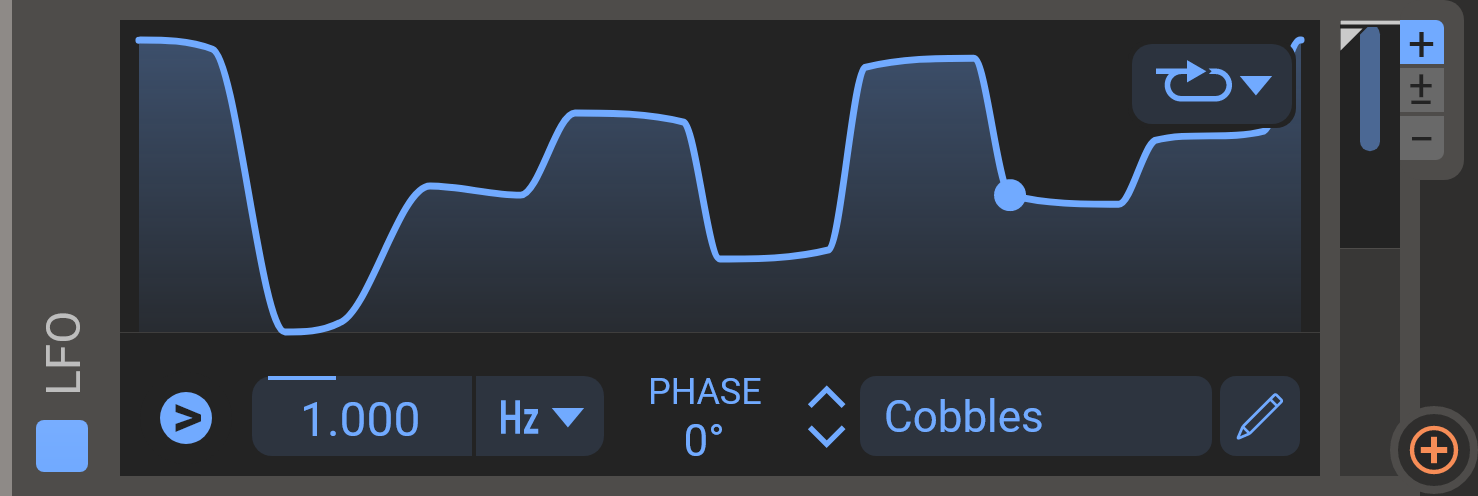 The LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator) module is one of the modulator modules you can add in the modulator lane at the bottom of the screen. They are ideal for modulating parameters in an oscillating and rhythmic fashion. The LFOs are very versatile since you can design your own LFO shapes. The LFO editor is described in detail in the curve editor chapter.
The LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator) module is one of the modulator modules you can add in the modulator lane at the bottom of the screen. They are ideal for modulating parameters in an oscillating and rhythmic fashion. The LFOs are very versatile since you can design your own LFO shapes. The LFO editor is described in detail in the curve editor chapter.
- Trigger
- This is meant as a modulation target for remotely triggering the LFO to restart. Right-clicking on the trigger button will bring up the triggering menu. The modulation triggering functionality is described in detail in the triggering chapter.
- Frequency
- Controls the speed of the oscillator, either in Hertz when in free running mode, or as a note length when running in synced mode.
- Phase
- Adjusts the phase offset of the LFO.
- Shape
- The LFO has a vast array of predefined shapes. Clicking on the name of the default shape will take you to a list of available shapes, organized in folders. You can also edit the LFO curve yourself in the LFO editor.
LFO Table
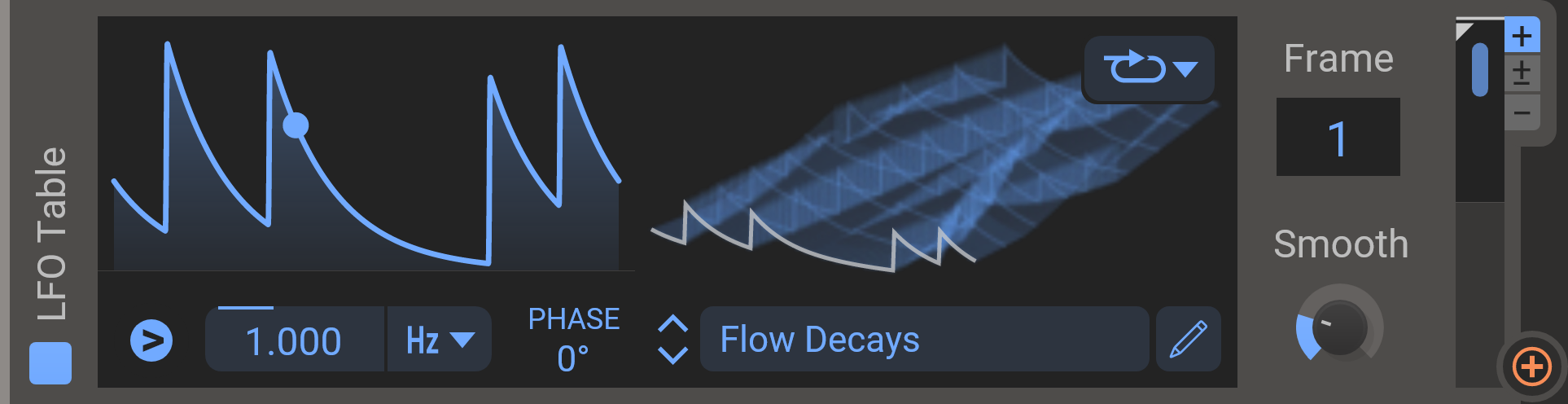 This modulator takes modulation design to the next level. By using a wavetable as a modulation source, it allows you to cycle through 256 LFO shapes in one modulator. This unique modulator opens up all kinds of possibilities. Use it to store a bank of rhythmical variations, or a variety of melodic sequences, or any other wild idea you can come up with. When combined with a Random modulator, LFO Tables are wonderful for crafting evolving generative patterns.
This modulator takes modulation design to the next level. By using a wavetable as a modulation source, it allows you to cycle through 256 LFO shapes in one modulator. This unique modulator opens up all kinds of possibilities. Use it to store a bank of rhythmical variations, or a variety of melodic sequences, or any other wild idea you can come up with. When combined with a Random modulator, LFO Tables are wonderful for crafting evolving generative patterns.
There are hundreds of wavetables to choose from, and you can even edit them or create your own. The wavetable table editor is described in detail in the wavetable editor chapter.
- Trigger
- This is meant as a modulation target for remotely triggering the LFO to restart. Right-clicking on the trigger button will bring up the triggering menu. The modulation triggering functionality is described in detail in the triggering chapter.
- Frame
- Lets you scroll through the 256 frames in the wavetable.
- Smooth
- Reduces the scope and the depth of a wavetable. Higher values flattens the wavetable curve.
Curve
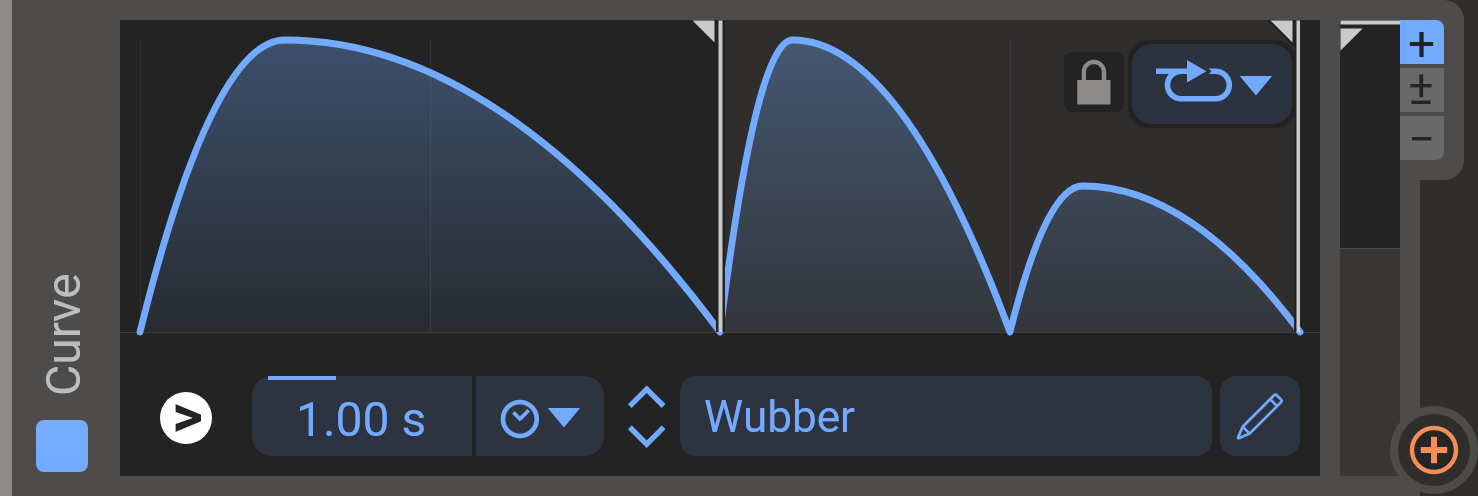 The curve modulator is quite simlilar to the envelope modulator above.
The curve modulator is quite simlilar to the envelope modulator above.
You can choose from a large number of curves, all logically sorted in folders. Those curves can be tweaked in the curve editor available under the pen symbol. This editor is described in detail in the curve editor chapter.
The curve graph has two handles that allow you to set loop points within the curve, while the loop symbol lets you select the desired loop mode.
- Trigger
- This is meant as a modulation target for remotely triggering the LFO to restart. Right-clicking on the trigger button will bring up the triggering menu. The modulation triggering functionality is described in detail in the triggering chapter.
- Modulator Rate
- Sets the rate of the modulator. The total time to complete one cycle is displayed in seconds. You can set the speed to be freewheeling or synced to the DAW clock.
- Lock
- Locks the loop settings to the current values when loading curves.
- Curve Editor
- The pen symbol opens the curve editor. Read more about the editor in the Curve Editor chapter.
Random
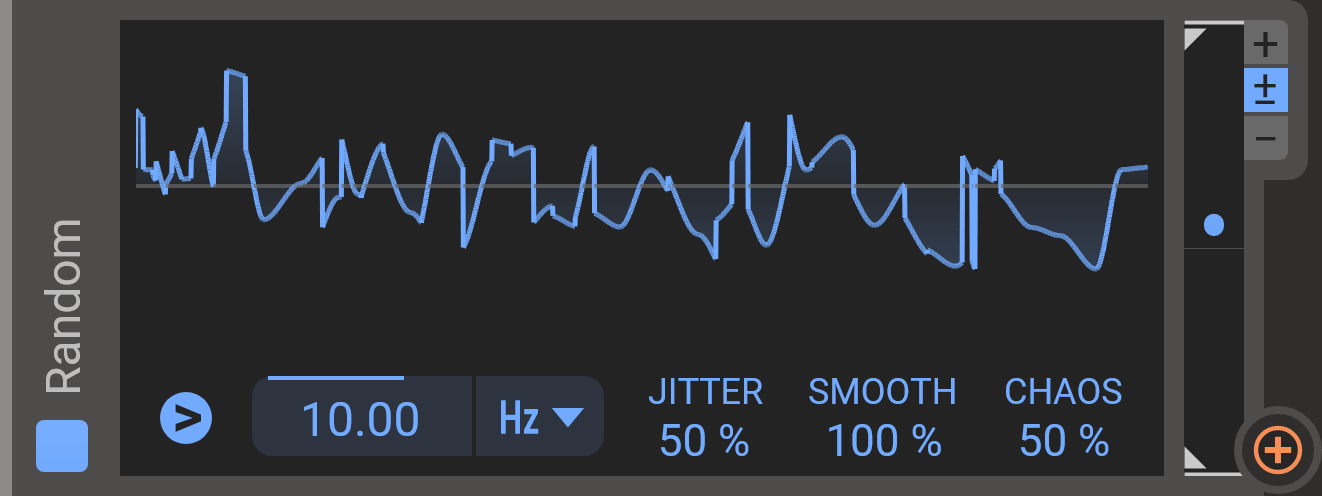 This module outputs a stream of random values that can be used to create random movement in your patch. For polyphonic patches, the random modulator will output different random values for each voice.
This module outputs a stream of random values that can be used to create random movement in your patch. For polyphonic patches, the random modulator will output different random values for each voice.
- Trigger
- This is meant as a modulation target for remotely triggering the LFO to restart. Right-clicking on the trigger button will bring up the triggering menu. The modulation triggering functionality is described in detail in the triggering chapter.
The Random module has an additional setting in this menu called voice mode, which adjusts how the random sequence is seeded with the following values:
- Unison
- Voices triggered together (for example a chord or by global unison, as well as the global modulator) will all use the same random sequence.
- Independent
- Every voice and the global modulator will use an independent random sequence. This matches the behavior of Phase Plant v1.8 and earlier, and presets made with these versions will load with this mode selected.
- Frequency
- Controls how often new random values are picked, either in Hertz when in free running mode, or as a note length when running in synced mode.
- Jitter
- Randomly adjusts the timing for when values are picked, making the modulator less rhythmic.
- Smooth
- Blends between the random numbers to create a smooth sequence instead of a stepped one.
- Chaos
- Adjust the length of each random step. For lower chaos values, the next random value will be closer to the previous one. At 0 the random value will update only on triggers, and then stay the same until the next trigger event.
Audio Follower
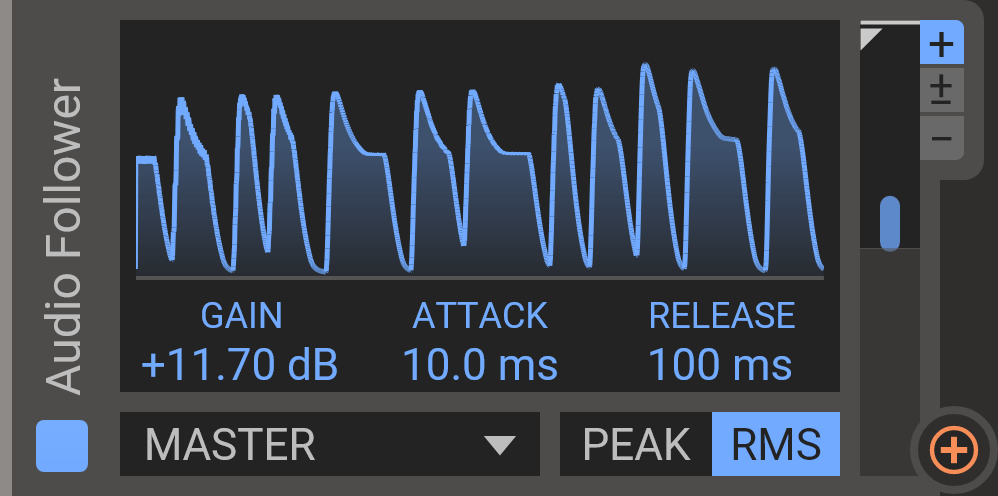 Tracks the amplitude of an incoming audio signal and generates a modulation signal based on that. Input can be selected in the lower left corner: Lane 1–3, Master, or Sideband.
Tracks the amplitude of an incoming audio signal and generates a modulation signal based on that. Input can be selected in the lower left corner: Lane 1–3, Master, or Sideband.
- Gain
- Tweak the volume of the followed signal to get a good output range.
- Attack
- How quickly the output ramps up when input increases.
- Release
- How quickly the output falls off when input goes down.
In Phase Plant Audio Follower can be used to convert some audio rate modulation sources to control rate. Please note that this still does not cause any control rate modulation targets to update on every sample.
Pitch Tracker
![]() Tracks the pitch of an incoming audio signal and generates a modulation signal based on that. Input can be selected in the lower left corner: Lane 1–3 or Master or Sideband.
Tracks the pitch of an incoming audio signal and generates a modulation signal based on that. Input can be selected in the lower left corner: Lane 1–3 or Master or Sideband.
- Keyboard graph
- The vertical sliders in the graph allow you to set a range and a center frequency.
- Sensivity
- Low sensitivity gives more stable results and higher values allows for faster changes to the output.
Note
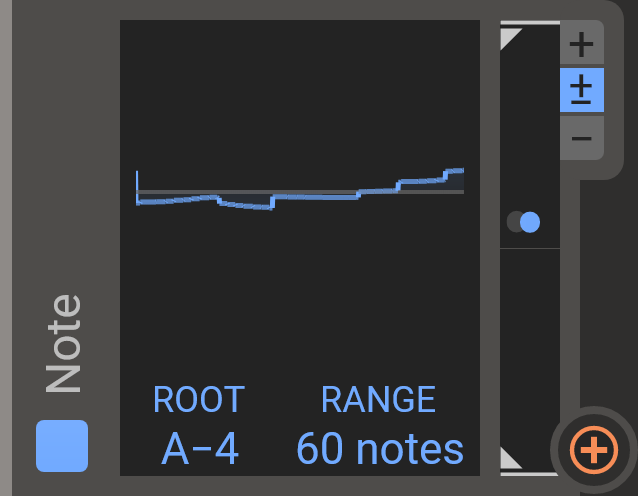 This modulator lets you use the played note as a modulation source. The range of this modulator is tuned to be the same as many of the cutoff and frequency knobs you will come across in Phase Plant and in the Snapins. This means that if you modulate these parameters at 100%, they will perfectly track the note you play.
This modulator lets you use the played note as a modulation source. The range of this modulator is tuned to be the same as many of the cutoff and frequency knobs you will come across in Phase Plant and in the Snapins. This means that if you modulate these parameters at 100%, they will perfectly track the note you play.
Polyphonic pitch bend will effect the modulation signal of the Note modulator.
Pressure
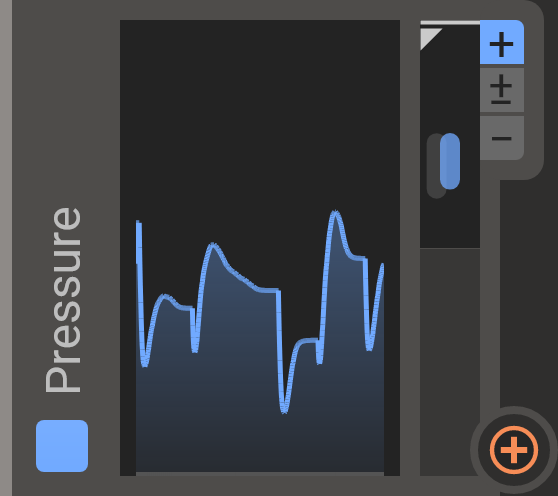 This modulator reflects pressure data from a MIDI controller, I.E. with how much force you are holding your keys down. It can receive it's data from various sources; the "channel pressure" MIDI CC, as well as "polyphonic aftertouch" MIDI messages. If you are using VST3 it additionally exposes a "Polyphonic Expression" slot to your DAW.
This modulator reflects pressure data from a MIDI controller, I.E. with how much force you are holding your keys down. It can receive it's data from various sources; the "channel pressure" MIDI CC, as well as "polyphonic aftertouch" MIDI messages. If you are using VST3 it additionally exposes a "Polyphonic Expression" slot to your DAW.
Pressure is an MPE compatible modulator, and if your DAW supports polyphonic expressions this module can have a different pressure for each played note.
Velocity
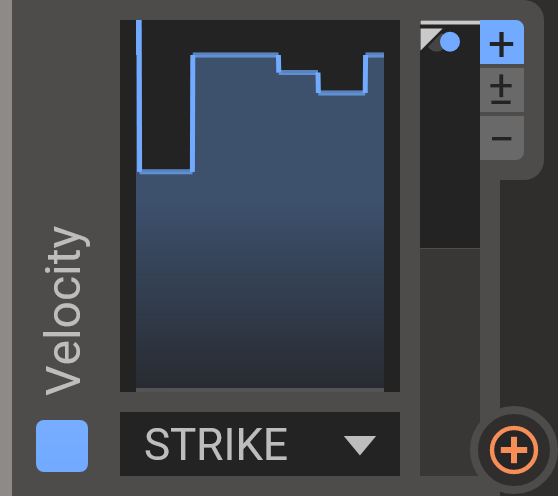 This modulator tracks the velocity of each played note (how hard the note was initially struck). Use this to make your patches velocity sensitive so they can be played both softly and loudly. It can also be used to track release velocity, which is available on some MIDI controllers.
This modulator tracks the velocity of each played note (how hard the note was initially struck). Use this to make your patches velocity sensitive so they can be played both softly and loudly. It can also be used to track release velocity, which is available on some MIDI controllers.
Pitch Wheel
 This modulator tracks the pitch wheel of your keyboard or controller if available.
This modulator tracks the pitch wheel of your keyboard or controller if available.
When using MPE the pitch wheel module will only track the pitch wheel on the global channel. Polyphonic pitch bends can be picked up by the Note modulator.
Note Gate
 The note-on and note-off messages from your MIDI controller will generate signals for this modulator.
The note-on and note-off messages from your MIDI controller will generate signals for this modulator.
MIDI CC
 Any MIDI continuous controller can be used as a modulator. After instantiating this module, you will be asked to move a controller. Once detected, this controller will be bound to the module. To assign another controller, just click the bottom text field.
Any MIDI continuous controller can be used as a modulator. After instantiating this module, you will be asked to move a controller. Once detected, this controller will be bound to the module. To assign another controller, just click the bottom text field.
MPE Timbre
 MPE controllers commonly have a third axis of polyphonic control on each key. Typically activated by moving your finger up and down on the key. The MPE Timbre module lets you use this polyphonic data for modulations.
MPE controllers commonly have a third axis of polyphonic control on each key. Typically activated by moving your finger up and down on the key. The MPE Timbre module lets you use this polyphonic data for modulations.
Remap
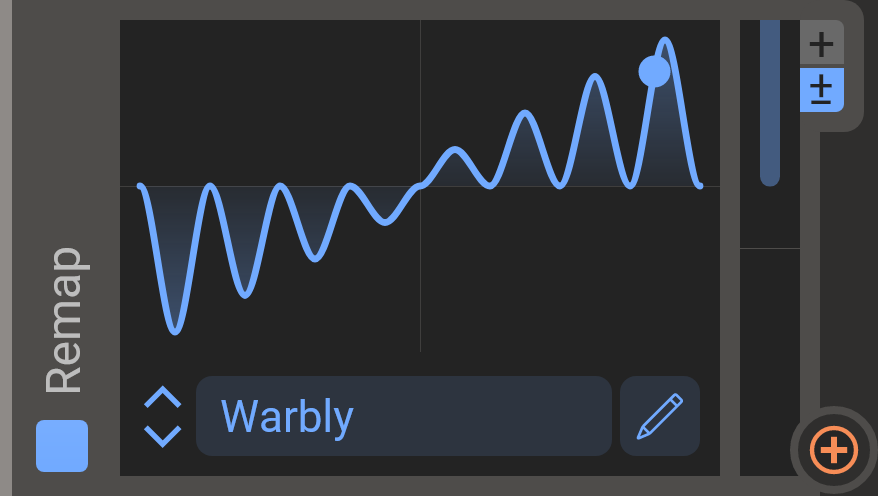 Map incoming values to whatever output values you need with custom remap shapes. Remap brings you even more precise control over your modulation. If you connect this module between an LFO and a generator, Remap can tweak the LFO curve in all possible ways. As usual, there are numerous scales and curves to choose from, and the editor allows you to edit them freely. Detailed info about the curve editor can be found in the curve editor chapter.
Map incoming values to whatever output values you need with custom remap shapes. Remap brings you even more precise control over your modulation. If you connect this module between an LFO and a generator, Remap can tweak the LFO curve in all possible ways. As usual, there are numerous scales and curves to choose from, and the editor allows you to edit them freely. Detailed info about the curve editor can be found in the curve editor chapter.
Lower Limit / Upper Limit
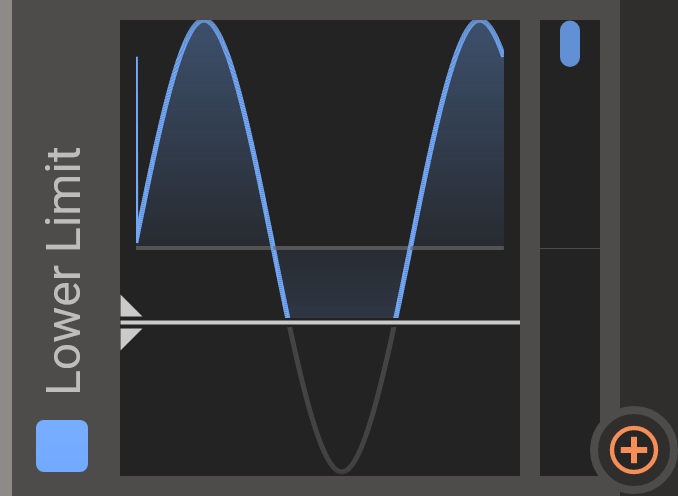 The Lower- and Upper Limit modules can be used to clamp the output of another modulator so that it never goes outside certain values. The white bar in the middle can be moved vertically and the graph will illustrate how the value stays within the limits.
The Lower- and Upper Limit modules can be used to clamp the output of another modulator so that it never goes outside certain values. The white bar in the middle can be moved vertically and the graph will illustrate how the value stays within the limits.
Remember that you can modulate the limits when relevant.
Scale
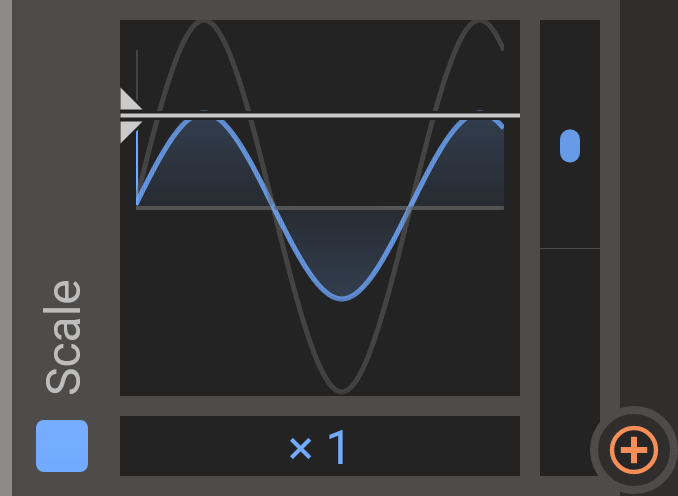 Adjust the output of another modulator with the Scale modulator by moving the white handle vertically. You can use the bottom multiplier control to change the order of magnitude.
Adjust the output of another modulator with the Scale modulator by moving the white handle vertically. You can use the bottom multiplier control to change the order of magnitude.
Remember that you can modulate the scale factor when relevant.
Sample & Hold
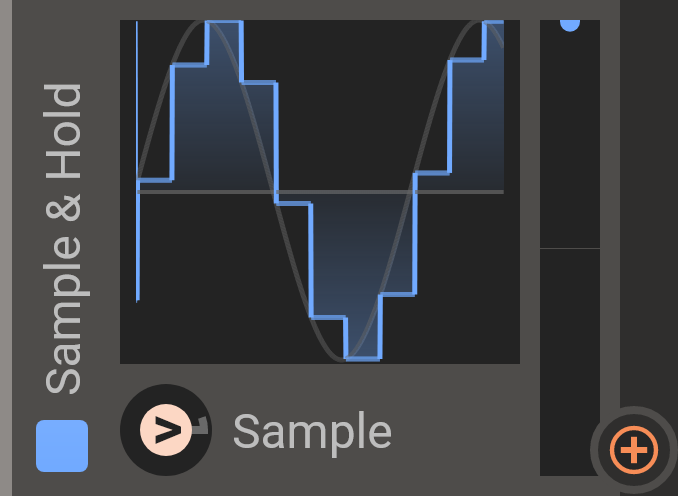 Samples a value from an input signal when triggered, and outputs that value constantly until triggered again. Connect an input signal by sending as a modulation to the center graph area, and the trigger signal in the same way to the trigger arrow (>).
Samples a value from an input signal when triggered, and outputs that value constantly until triggered again. Connect an input signal by sending as a modulation to the center graph area, and the trigger signal in the same way to the trigger arrow (>).
Every time the trigger signal rises past the threshold (which can be changed by right-clicking on the trigger arrow) a new value will be sampled from the input signal at that moment. That value will be held and output from the module until a new trigger occurs.
The modulation triggering functionality is described in detail in the triggering chapter.
Triggering
Many of the modulation modules have a trigger button. The trigger button (>) can be use to trigger a modulator and restart its cycle. The trigger input is actually a gate, i.e. it it will turn on when you press it and turn off when you release it. It will restart the modulator from zero when turned on, and perform its sustain action until the gate is released (for envelopes or LFOs/Curves with sustain loop mode, for example).
By default, the trigger gate is controlled by the note, turning it on when a note is struck and turning it off when the note is released. This behavior be changed (see below)
When modulation is attached to the trigger, it will stop being triggered by notes and instead only by the modulation (and clicks). This behavior be changed (see below).
Right-clicking on a modulation trigger button will bring up the trigger menu, where you can adjust the trigger sensitivity for when the trigger is modulated. You can also change the behavior for when notes trigger the modulator:
- Auto
- The default setting, notes do not trigger the modulator when a modulation is attached to the trigger. Otherwise, this mode selects between "Always" and "Legato" depending on the polyphony setting in the Phase Plant voice settings.
- Never
- Notes never trigger the modulator. You can use this setting to create a free running LFO.
- Always
- The modulator is triggered by every note-on.
- Legato
- The modulator is triggered by the first note in a group of legato notes, but will not be triggered again until all notes are released.