Kilohearts Essentials
Designed to be combined
Common controls
3-Band EQ
Bitcrush
Channel Mixer
Chorus
Comb Filter
Compactor
Compressor
Delay
Distortion
Dynamics
Ensemble
Filter
Flanger
Formant Filter
Frequency Shifter
Gain
Gate
Haas
Ladder Filter
Limiter
Nonlinear Filter
Phase Distortion
Phaser
Pitch Shifter
Resonator
Reverb
Reverser
Ring Mod
Stereo
Shaper
Tape Stop
Trance Gate
Transient Shaper
Overview

Kilohearts Essentials is a free collection of Kilohearts Snapins. Snapins are individual audio effect modules, each performing a specific task.
Designed to be combined
The Kilohearts Ecosystem give you the freedom to combine these Snapins in infinite different ways in order to create interesting and unique modular effects. Snapins can be also loaded individually into your DAW as a standard VST, AAX or AU plugin.
Kilohearts Snapins are designed with simplicity in mind and with the expressed purpose of giving you the ability to "build your own" plugins from these building blocks. They are optimised to be CPU-efficient so they can be stacked together without melting your computer. Load one of our host plugins and try a few factory presets to get a feel for what you can do with these fundamental ingredients.
When using any of the Snapins in your everyday work it can be easy to forget the extensive modulation options available to you by using them inside one of the hosts instead. It can often be extremely useful to set up a Snap Heap patch with only a single Snapin in it to expand on it's possibilities a hundredfold.
Common controls
All Snapins have some features in common, all of them found in the header section.
- Power button
- Just to the left of the Snapin title is a blue square. It works as a checkbox to enable the plugin. When turned off, the plugin is bypassed and lets all incoming sound through unaffected.
- Minimize (not available in stand-alone mode)
- Just like all other Kilohearts modules, Snapins can be collapsed when you want to save screen space for something else.
- Preset bar
- If you click the small downwards arrow in the Snapin header, controls for handling presets will fold down. These controls let you see the name of the currently selected preset, as well as step through any other presets in the active folder of the associated preset browser. To see the full preset browser, click the little folder icon. The Snapins all have a little Dice icon in the preset bar that you can use to randomize all controls to explore the possibilities.
3-Band EQ
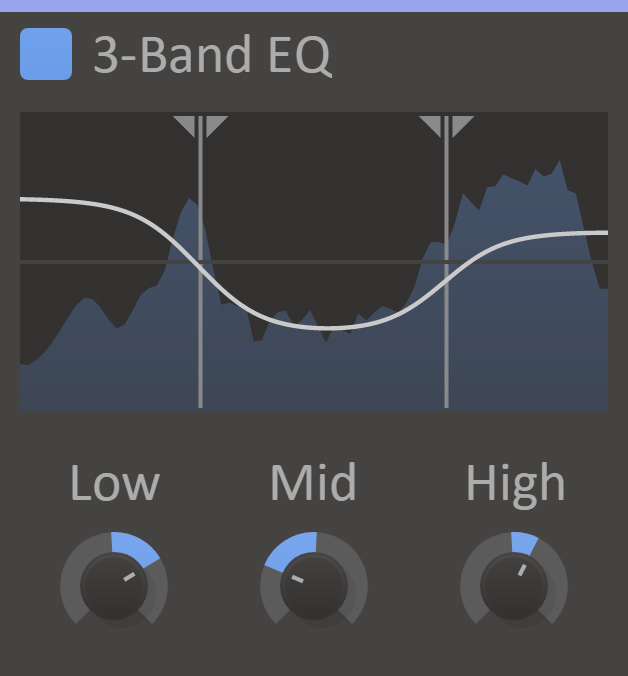 EQ 3-Band is a three band EQ with adjustable split frequencies.
EQ 3-Band is a three band EQ with adjustable split frequencies.
- Splits
- Adjusts cutoff frequency between low and mid, and between mid and high bands.
- Low
- Gain for low frequency (bass) band.
- Mid
- Gain for middle frequency (midrange) band.
- High
- Gain for high frequency (treble) band.
Bitcrush
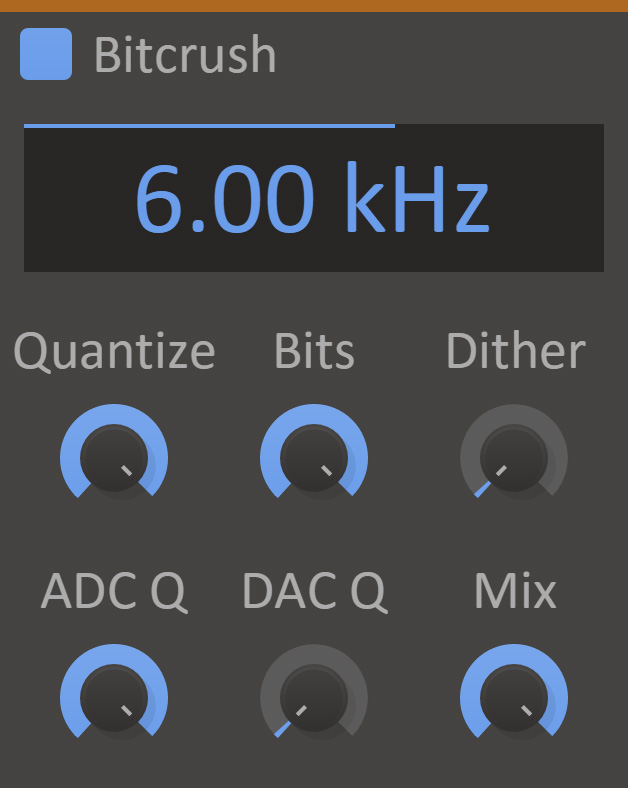 Bitcrush can be used to create distorting effects that sound like that of scraping analog radio, or inherently lo-fi sound sources, like old video games. It simulates the audio being sampled and replayed using a low quality sampler with limited sample rate and bit depth.
Bitcrush can be used to create distorting effects that sound like that of scraping analog radio, or inherently lo-fi sound sources, like old video games. It simulates the audio being sampled and replayed using a low quality sampler with limited sample rate and bit depth.
- Rate
- Down sample the signal to a minimum of 200 Hz.
- Bits
- Quantize the amplitude of each sample of the signal. A lower value will result in a more distorted sound.
- ADC Q
- Quality of the analog-to-digital conversion. A lower value will add dissonant aliasing in the low frequencies.
- DAC Q
- Quality of the digital-to-analog conversion. A lower value will add dissonant aliasing in the high frequencies.
- Dither
- Adds noise to the signal in order to reduce distortion caused by quantization.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Channel Mixer
 Channel Mixer gives you control over the amplitude of both stereo channels respectively, and also the option to cross-mix them into each other.
Channel Mixer gives you control over the amplitude of both stereo channels respectively, and also the option to cross-mix them into each other.
- Left to Left
- Scales the amplitude of the incoming left stereo channel from -1 (phase inverted) through 0 (silent) to 1 (passthrough).
- Right to Left
- Scales the amplitude of the incoming right stereo channel, but outputs it to the left channel.
- Left to Right
- Scales the amplitude of the incoming left stereo channel, but outputs it to the right channel.
- Right to Right
- Scales the amplitude of the incoming right stereo channel, and outputs it to the right channel.
Chorus
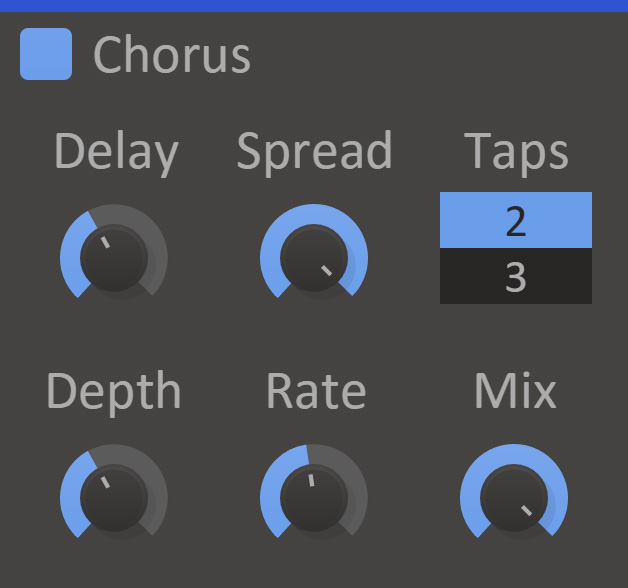 Chorus enhances the stereo effect and presence of a sound by mixing it with delayed versions of itself.
Chorus enhances the stereo effect and presence of a sound by mixing it with delayed versions of itself.
- Delay
- The average delay for the delayed voices.
- Rate
- The frequency of how fast to vary the delay.
- Depth
- How much to vary the delay.
- Spread
- Stereo width of the effect. A lower value will go towards a mono output.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Taps
- The number of chorus voices.
Comb Filter
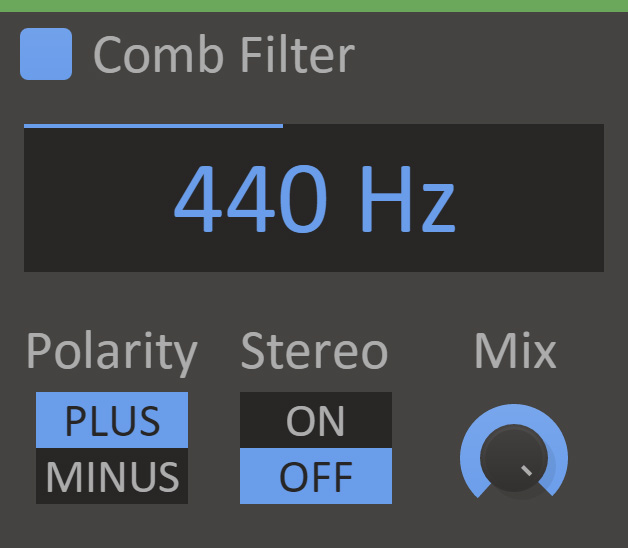 Comb Filter will mix the signal with a delayed version of itself, creating a filter with repeated troughs and peaks across the spectrum.
Comb Filter will mix the signal with a delayed version of itself, creating a filter with repeated troughs and peaks across the spectrum.
- Cutoff
- Cutoff setting for the filter, the distance between each peak.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Polarity
- The polarity setting swaps troughs for peaks and vice versa, with the plus setting having a peak at 0 Hz, and the minus setting a trough at 0 Hz.
- Stereo
- The stereo setting flips the polarity setting for the right channel, allowing the the comb filter to be used for mono compatible stereo widening.
Compressor
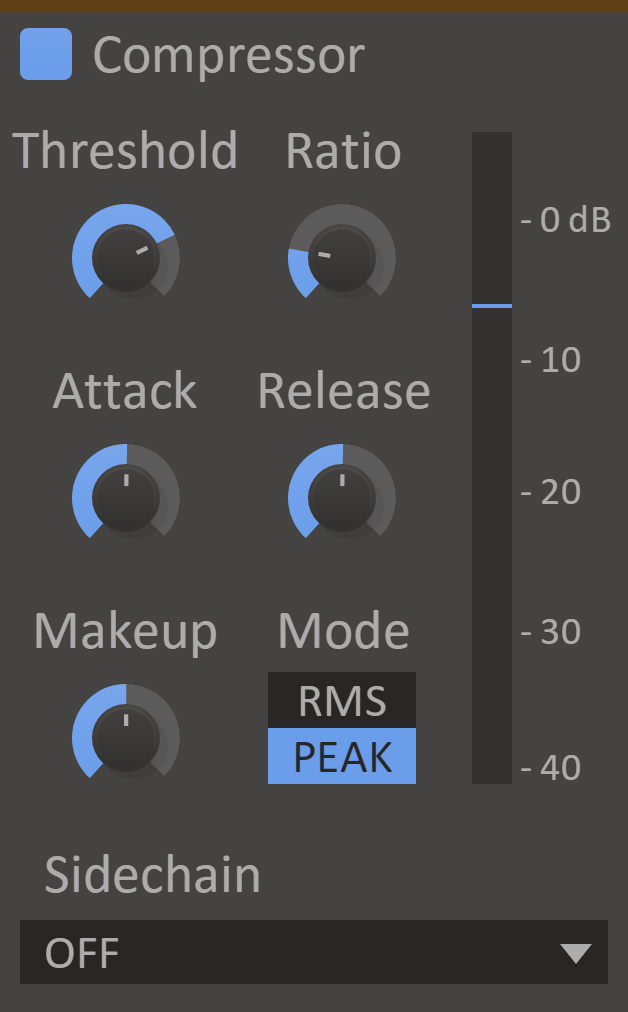 Compressor will even out the audio volume by lowering the volume when the signal is loud.
Compressor will even out the audio volume by lowering the volume when the signal is loud.
- Attack
- The attack time is the time it takes to lower the volume when the input volume is over the threshold.
- Release
- The release time is the time it takes to return the volume to normal when the input volume is under the threshold.
- Mode
- In RMS mode the compressor will measure the volume using the root mean square method, which gives an accurate measurement of audio power. In peak mode the compressor will follow the peaks in the audio waveform, which makes it more responsive to transients.
- Ratio
- The ratio decides how much the compressor will reduce the audio volume. At 1:2, for example, the volume will be lowered until it is halfway between the input volume and the threshold.
- Threshold
- The threshold for when the compressor will start lowering the volume.
- Makeup
- The makeup gain will increase the volume of the output signal to compensate for the loss in overall volume that the compressor causes.
- VU Meter
- Displays the current input level, the selected threshold, and the compressor's current attenuation.
- Sidechain
- When enabled attenuation is calculated based on a secondary input, but the effect is applied to the main input. (See our guide to setting up sidechains in all DAWs here)
Compactor
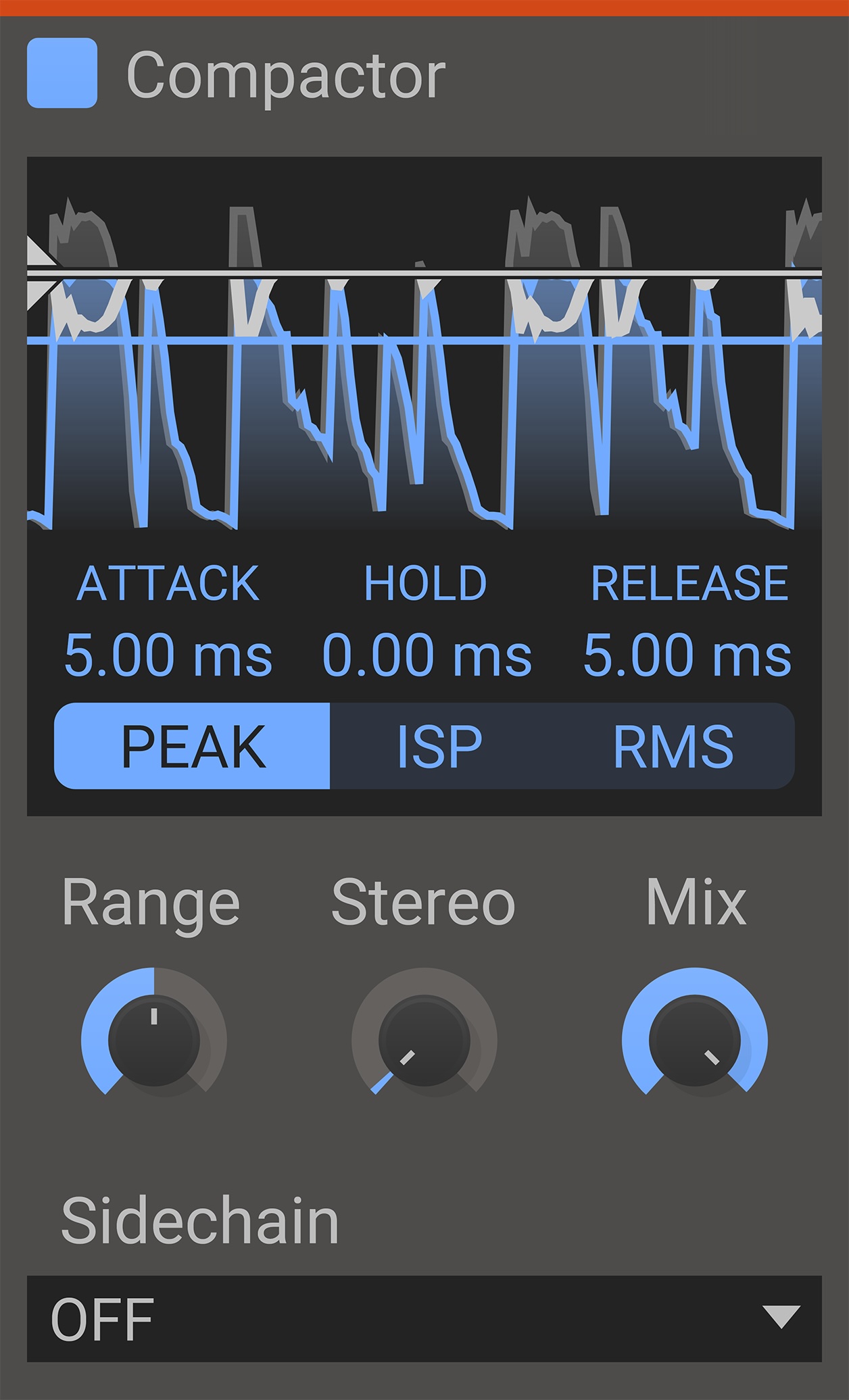 Compactor has several uses including ducking, clipping, and limiting. Use it without a sidechain input for limiting like functionality, and with a sidechain input to very exctly duck the signal based on the volume of the sidechain input.
Compactor has several uses including ducking, clipping, and limiting. Use it without a sidechain input for limiting like functionality, and with a sidechain input to very exctly duck the signal based on the volume of the sidechain input.
- Attack
- The attack value decides how far ahead the audio is ducked. A higher value will start ducking earlier.
- Hold
- The hold value decides for how long the signal is ducked once the input is no longer above the threshold.
- Release
- The release value sets how long it takes for the audio to return to full volume once the input no longer passes the threshold and the hold stage has finished.
- Threshold
- When sidechain level reaches the threshold the input will be silenced. When there is no sidechain the input will be limited to the threshold level.
- Mode
- In RMS mode Compactor will measure the volume using the root mean square method, which gives an accurate measurement of audio power. In PEAK mode Compactor will follow the peaks in the audio waveform on a per-sample basis, which ensures no peaks pass the threshold. In ISP mode Compactor will follow peaks all peaks in the audio waveform, even if they occur between samples.
- Range
- The range sets the range of the gain reduction. Values over 100% will exaggerate the effect.
- Stereo
- Adjusts the correlation in processing between left and right channels. At 0% both channels are processed the same. At 100% left and right channels are processed independently.
- Sidechain
- When enabled attenuation is calculated based on a secondary input, but the effect is applied to the main input. (See our guide to setting up sidechains in all DAWs here)
Delay
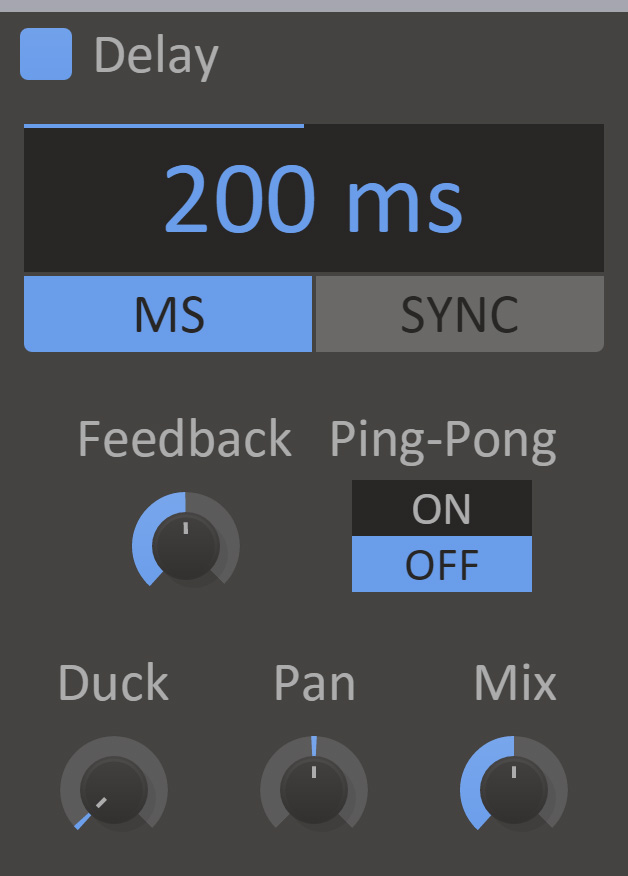 Delay will delay the input signal for an echoing effect.
Delay will delay the input signal for an echoing effect.
- Delay
- The amount of time beore the delayed sound starts playing. This will be expressed in milliseconds or as parts of a beat, depending on Sync Mode.
- Sync Mode
- When sync is enabled the delay time will be synchronized to the song tempo.
- Feedback
- The feedback setting will cause the delayed sound to feed back into the delay. This will create an exponentially decaying echo.
- Pan
- Adjust the panning of the delayed sound.
- Ping-Pong
- Swaps the left and the right channel of the delayed sound when it is fed back into the delay. When combined with panning this will make the echo bounce back and forth between the speakers.
- Duck
- When duck is turned up, the output volume from the delay will automatically be lowered when the input volume is high.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Distortion
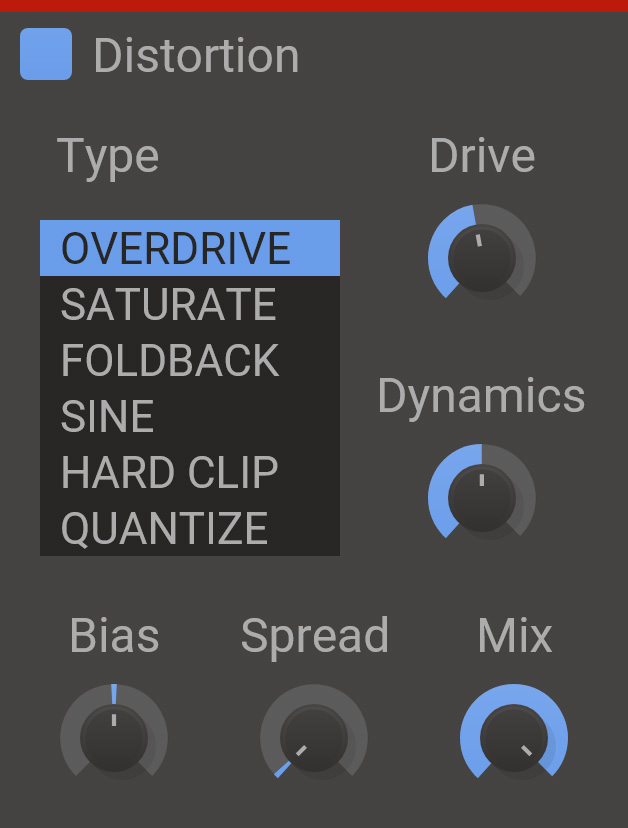 Distortion is a versatile distortion effect with a wide selection of algorithms.
Distortion is a versatile distortion effect with a wide selection of algorithms.
- Drive
- The drive setting will boost the input signal, causing a heavier distortion.
- Bias
- The bias will add a DC offset to the signal before distorting. Adding some bias can prevent the distorted audio from sounding hollow and uninteresting.
- Spread
- The spread will add different amount of bias to the left and right channels. This can give some nice and subtle stereo widening.
- Type
- The flavor of distortion. Select between overdrive, saturate, foldback, sine, hard clip and quantize.
- Dynamics
- A common problem with distortion is that it can remove the dynamic content of the input signal, forcing the output to maximum volume. Turn up this knob to preserve the dynamics of the input.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Dynamics
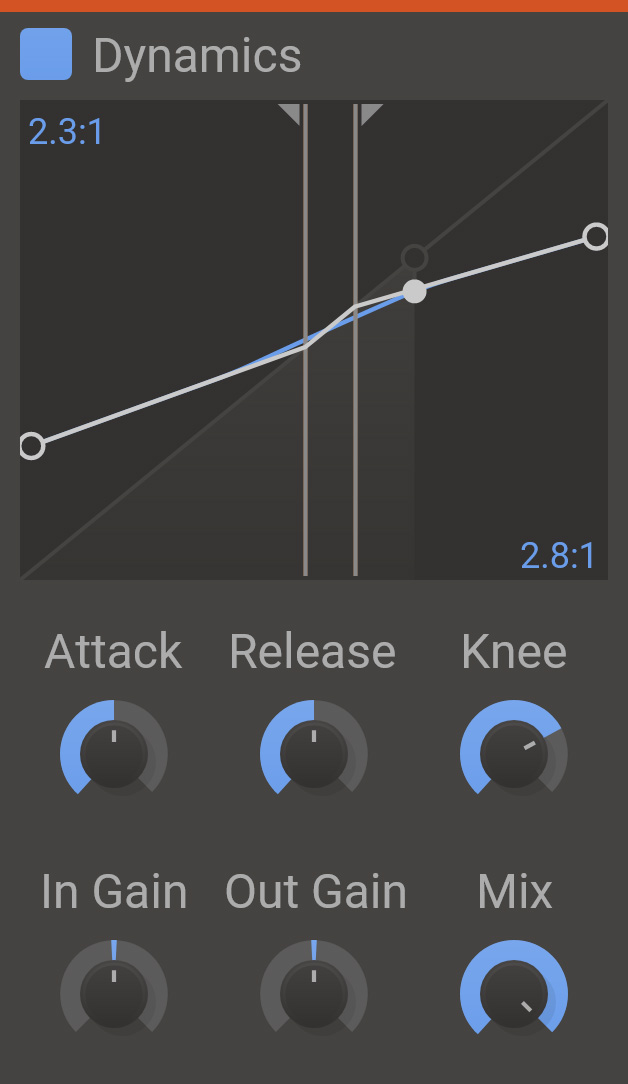 Dynamics processing featuring upward and downward compression as well as expansion. Thresholds and ratio are controlled by clicking and dragging on the visualization in the upper part of the plugin interface. The visualization shows how input levels are mapped to output levels by the dynamics processing. The current input and output levels are marked in the visualizer by a moving disc.
Dynamics processing featuring upward and downward compression as well as expansion. Thresholds and ratio are controlled by clicking and dragging on the visualization in the upper part of the plugin interface. The visualization shows how input levels are mapped to output levels by the dynamics processing. The current input and output levels are marked in the visualizer by a moving disc.
- Low Threshold
- Low threshold for upwards compression and expansion.
- Low Ratio
- Ratio of upwards compression or expansion below the low threshold.
- High Threshold
- High threshold for downwards compression.
- High Ratio
- Ratio of downwards compression above the high threshold.
- Attack
- Adjusts attack time.
- Release
- Adjusts release time.
- Knee
- Smoothes the knee of the compression curve across the thresholds.
- In Gain
- Adjusts gain for the incoming signal.
- Out Gain
- Adjusts gain after compression.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Ensemble
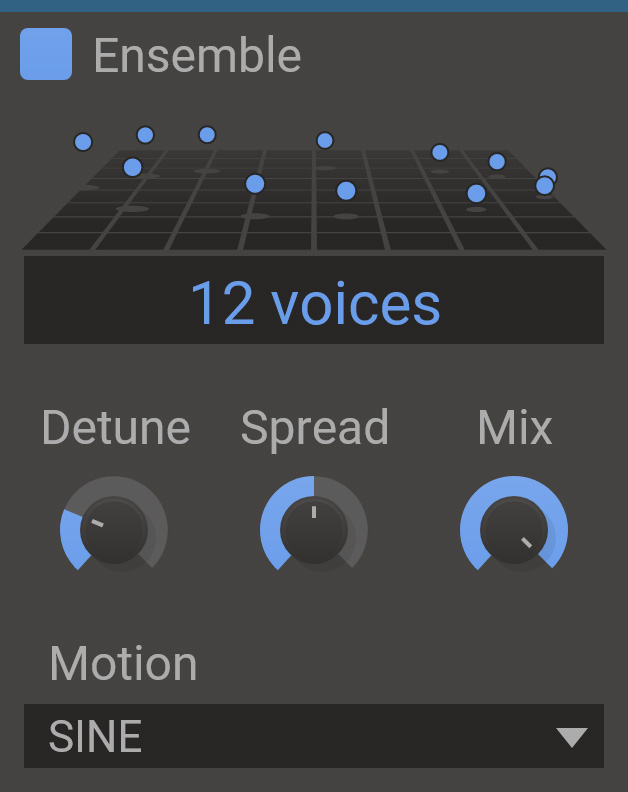 Ensemble creates the illusion of many voices playing in unison. Much like a chorus it creates this effect by playing delayed copies of the incomping sound. On top of this it also modulates the phases of each voice to create a silky smooth result without any metallic flanging. The delay times for each voice is also modulated in order to detune each voice slighty.
Ensemble creates the illusion of many voices playing in unison. Much like a chorus it creates this effect by playing delayed copies of the incomping sound. On top of this it also modulates the phases of each voice to create a silky smooth result without any metallic flanging. The delay times for each voice is also modulated in order to detune each voice slighty.
- Voices
- Number of voices to play simultaneously.
- Detune
- How quickly to modulate the delay for each voice, affecting how detuned the voices will be.
- Spread
- Pans voices left or right for a stereo effect.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Motion
- Selects between different patterns for the modulations of the voices.
Filter
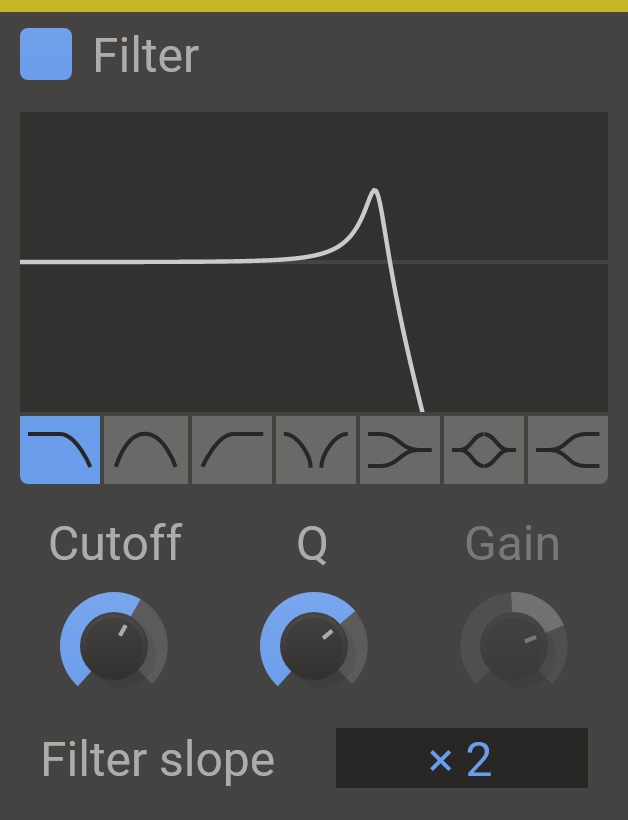 Filter provides a selection of common filters.
Filter provides a selection of common filters.
- Type
- The type of filter. Select between low pass, band pass, high pass, notch, low shelf, peak and high shelf filters.
- Cutoff
- The operating frequency of the filter. In a low-pass filter this is the frequency where the signal is reduced by 3dB.
- Q
- The filter Q setting. High values for Q will make the filter resonate at the cutoff frequency.
- Gain
- The gain value for the low shelf, peak and high shelf filter types.
- Filter slope
- The slope of the filter cutoff, with 1x representing a classic 2-pole filter.
Flanger
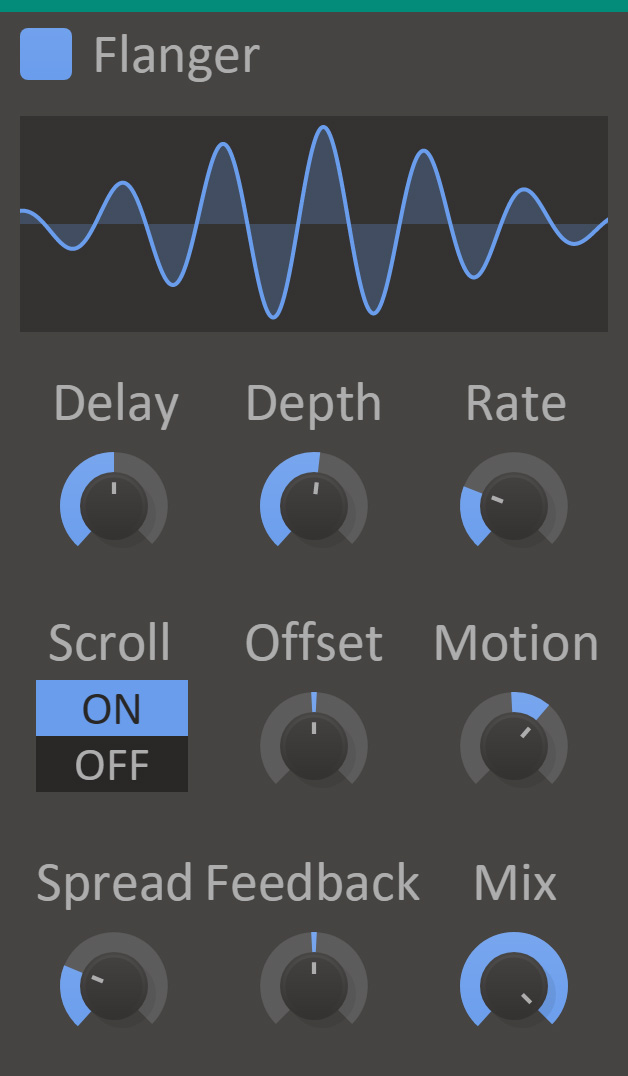 Creates a flanging effect by mixing the audio with a slightly delayed version of itself. The length of the delay can be adjusted manually and modulated. Optionally, this effect can also add a phase shift between the dry and wet signals to create an infinte barberpole-style flanging effect upwards or downwards.
Creates a flanging effect by mixing the audio with a slightly delayed version of itself. The length of the delay can be adjusted manually and modulated. Optionally, this effect can also add a phase shift between the dry and wet signals to create an infinte barberpole-style flanging effect upwards or downwards.
- Delay
- Adjusts the minimum delay.
- Depth
- Depth of delay modulation. Added on top of the minimum delay set by the delay knob.
- Rate
- Rate of delay modulation.
- Scroll
- Enables the phase offset and motion functions of the effect.
- Offset
- Phase offset between dry and wet signals.
- Motion
- Rate of modulation for the phase offset.
- Spread
- Stereo spread between left and right channels. Affects delay modulation and phase offset.
- Feedback
- Feedback of the wet signal back into the delay line.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Formant Filter
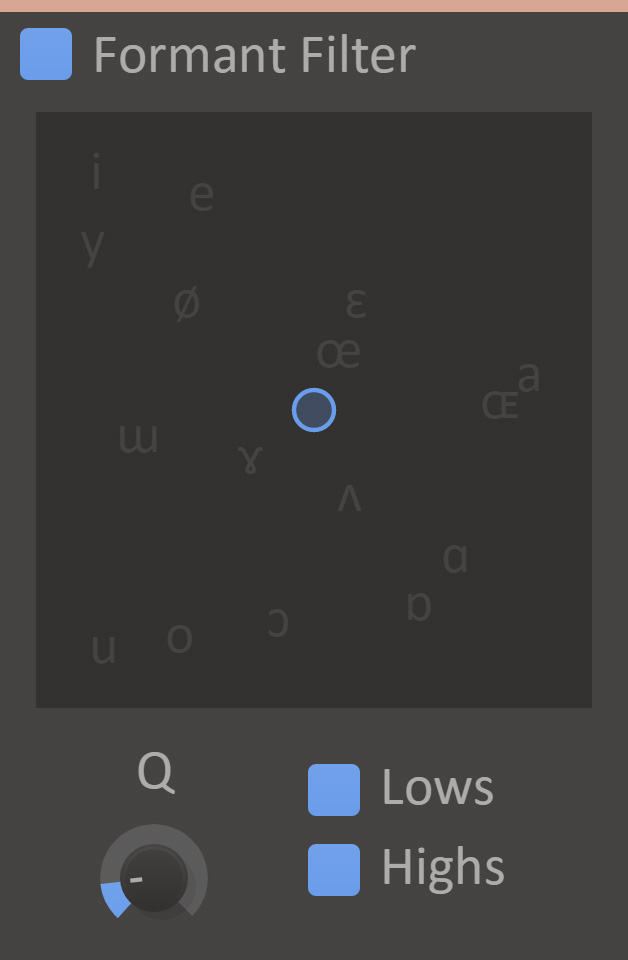 Formant Filter will boost two frequencies to mimic the sounds of different vowels.
Formant Filter will boost two frequencies to mimic the sounds of different vowels.
- Vowel Selector
- Selects two frequencies to boost.
- Q
- Adjust how powerful and narrow the frequency boost is.
- Lows
- Allow low frequencies through the filter.
- Highs
- Allow high frequencies through the filter.
Frequency Shifter
 Frequency Shifter will shift all the frequencies in the input signal up or down by a certain amount. This kind of shifting will ruin the harmonic content of the input signal, making it sound dissonant.
Frequency Shifter will shift all the frequencies in the input signal up or down by a certain amount. This kind of shifting will ruin the harmonic content of the input signal, making it sound dissonant.
- Shift
- How much to shift all frequencies by.
Gain
 Gain will increase or decrease the volume of a signal.
Gain will increase or decrease the volume of a signal.
- Gain
- Set how much to increase or decrease the volume, in decibels.
- VU Meter
- Displays the current output level on the left and right channels.
Gate
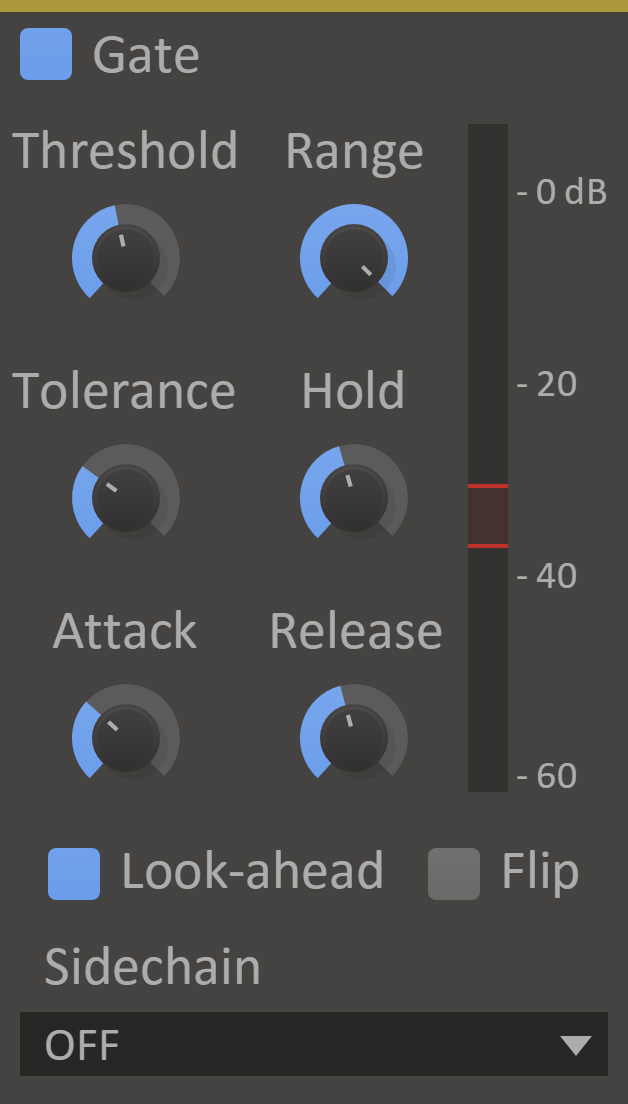 Gate will only let audio through when the input level is above a set threshold.
Gate will only let audio through when the input level is above a set threshold.
- Attack
- The attack time is the time it takes to for the gate to fully open when the input volume is over the threshold.
- Hold
- The hold time is the minimum time the gate will stay open.
- Release
- The release time is the time it takes to for the gate to fully close when the input volume is under the threshold.
- Threshold
- The volume threshold for when the gate will open.
- Tolerance
- A hysteresis range requiring the volume to drop a set amount of dB under the threshold before closing.
- Range
- The amount to attenuate the signal when the gate is closed.
- Look-ahead
- When enabled, a 5ms look-ahead will be used, allowing transients through at the cost of latency.
- Flip
- When flipped, the gate will act in reverse attenuating the signal when the gate is open.
- VU Meter
- Displays the current input level, the selected threshold & tolerance, and the gate's current state.
- Sidechain
- When enabled transients are detected based on a secondary input, but the effect is applied to the main input. (See our guide to setting up sidechains in all DAWs here)
Haas
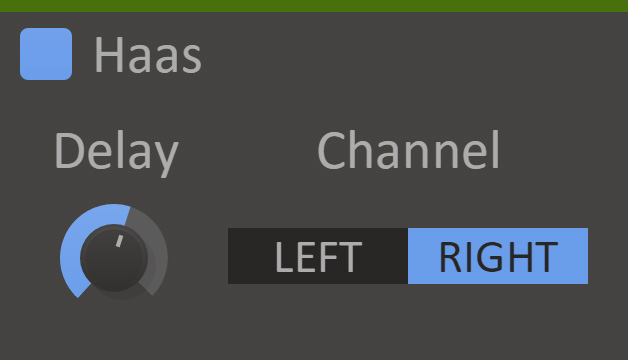 HAAS will widen the stereo of the audio by delaying the left or the right channel slightly.
HAAS will widen the stereo of the audio by delaying the left or the right channel slightly.
- Channel
- Which channel to delay.
- Delay
- The delay time.
Ladder Filter
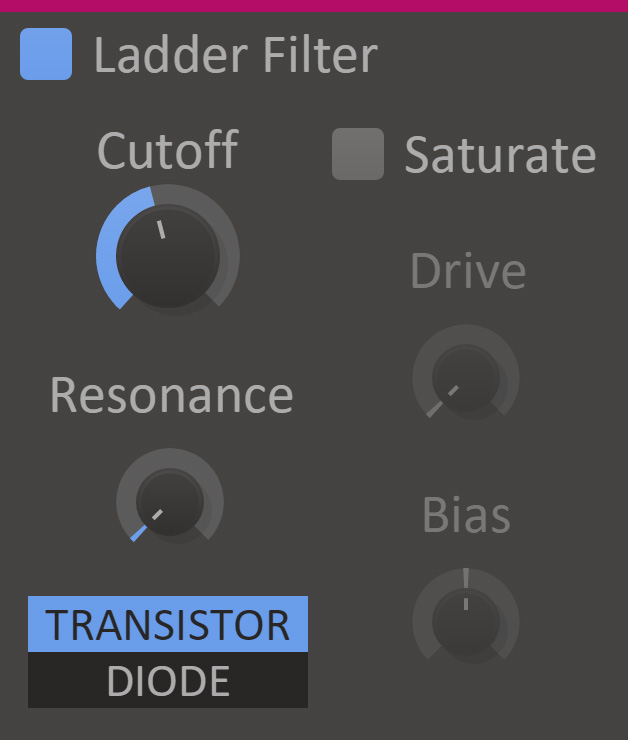 Ladder Filter simulates low pass filters found in classic hardware synths.
Ladder Filter simulates low pass filters found in classic hardware synths.
- Cutoff
- The filter cutoff frequency.
- Resonance
- The filter resonance setting. High values will make the filter resonate at the cutoff frequency.
- Topology
- Selects between transistor ladder and diode ladder topology. The diode ladder have a slightly more gentle rolloff after the cutoff frequency. The two topologies also behave differently when saturation is enabled.
- Saturate
- Simulates saturation of electronic components in the filter.
- Drive
- Simulates overdrive of the components in saturate mode.
- Bias
- Simulates bias voltage over the components in saturate mode.
Limiter
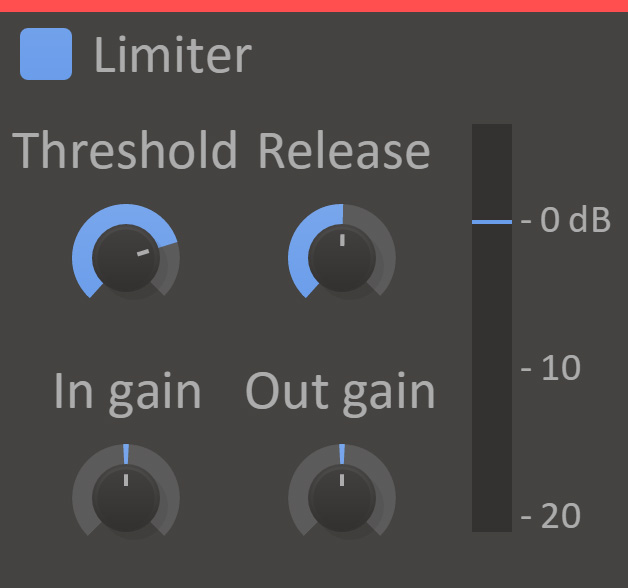 Limiter will prevent the audio volume from going over a certain threshold.
Limiter will prevent the audio volume from going over a certain threshold.
- In gain
- Gain to apply to the input signal before limiting.
- Out gain
- Gain to apply to the input signal after limiting.
- Threshold
- The maximum allowed volume.
- Release
- The release adjust how quickly the limiter returns the volume back to normal after limiting it due to a peak in the input volume.
- VU Meter
- Displays the current input level, the selected threshold, and the limiter's current attenuation.
Nonlinear Filter
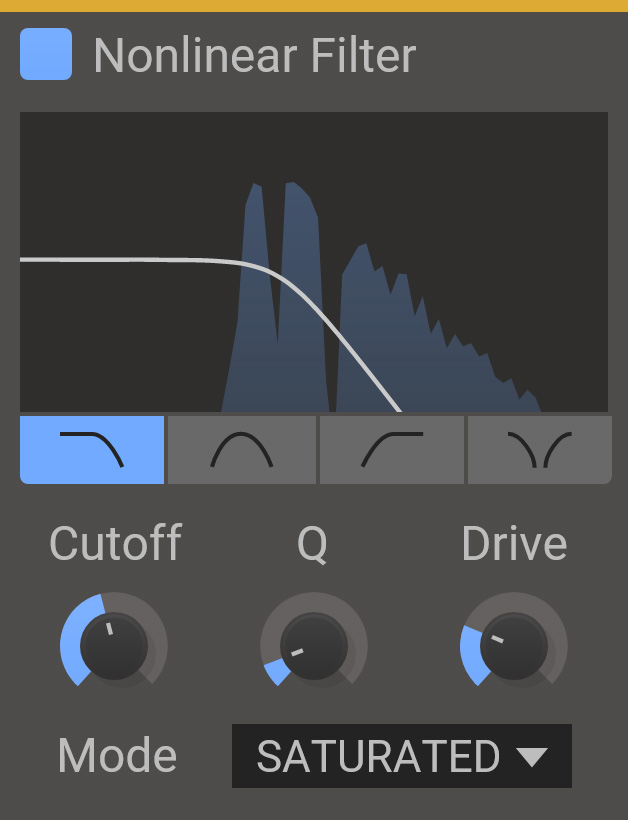 Nonlinear Filter colors and distorts the signal due to internal nonlinearities.
Nonlinear Filter colors and distorts the signal due to internal nonlinearities.
- Type
- The type of filter. Select between low pass, band pass, high pass and notch filters.
- Cutoff
- The operating frequency of the filter.
- Q
- The filter Q setting. High values for Q will make the filter resonate at the cutoff frequency.
- Drive
- Overdrives the filter, which makes the effect of the nonlinear behaviour more prominent.
- Mode
- Selects what flavor of nonlinearity you want. The clean mode has no nonlinearies, and does not color the signal. All other modes distort and color the signal in different ways to some extent.
Phase Distortion
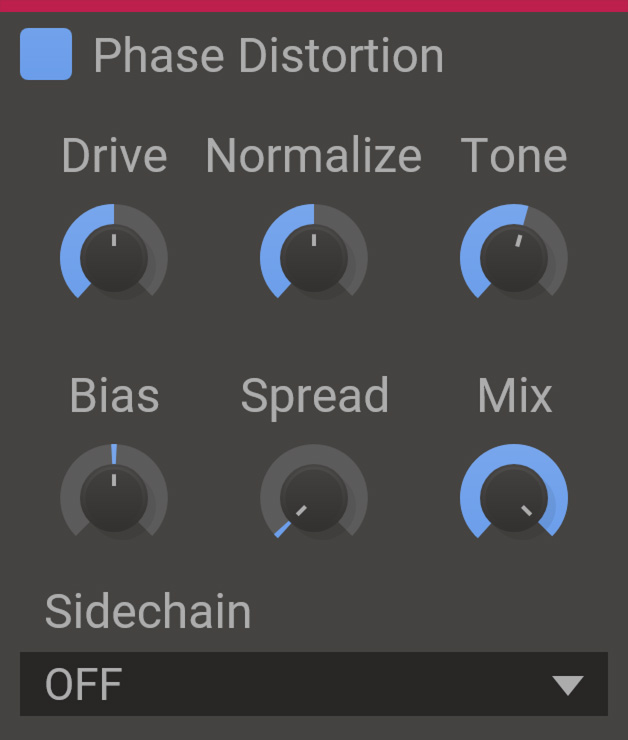 Phase Distortion distorts the signal by offseting the phases of the individual harmonics of the input signal. The amount of phase offset is controlled by the signal itself, much like FM feedback.
Phase Distortion distorts the signal by offseting the phases of the individual harmonics of the input signal. The amount of phase offset is controlled by the signal itself, much like FM feedback.
- Drive
- Controls the amount of distortion.
- Normalize
- Normalizes the signal, making the effect insensitive to input gain.
- Tone
- Filters the modulation to reduce high frequency noise.
- Bias
- Adds a constant phase offset to all harmonics.
- Spread
- Spreads phase offset for left and right channels for a stereo effect.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Phaser
 Phaser will filter the input signal, creating a series of moving peaks and troughs in the audio spectrum.
Phaser will filter the input signal, creating a series of moving peaks and troughs in the audio spectrum.
- Order
- A higher order setting will increase the order of the filters used by the phaser, creating a more pronounced effect with more peaks and troughs.
- Cutoff
- Sets the cutoff of the filters in the phaser, moving the peaks and troughs in the audio spectrum.
- Depth
- Adjusts the depth of modulation of the cutoff.
- Rate
- Adjusts the rate of modulation of the cutoff.
- Spread
- Adds a phase offset for the cutoff modulation between the left and right channels, for a stereo widening effect.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Pitch Shifter
 Pitch Shifter will adjust the pitch of the input signal up or down.
Pitch Shifter will adjust the pitch of the input signal up or down.
- Pitch
- How much to adjust the pitch, in semitones.
- Jitter
- How much randomness to add to the pitch. A high jitter setting can give a unison-like effect.
- Grain Size
- During processing the pitch shifter chops up the audio into small snippets called grains. This setting adjusts the length of the grains, which can influence the sound.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Resonator
 Resonator adds harmonic resonance to the input signal.
Resonator adds harmonic resonance to the input signal.
- Pitch
- The frequency at which to resonate.
- Decay
- Sets how long it takes for the resonance to ring out after the input goes silent.
- Intensity
- Adjusts how much the resonance amplifies the input signal.
- Timbre
- Switches between two different harmonic series for the resonance. Choose between all harmonics (saw tooth wave) or odd harmonics (square wave).
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Reverb
 Reverb adds the sense of space to any sound by emulating the sound bouncing off the walls in a physical room.
Reverb adds the sense of space to any sound by emulating the sound bouncing off the walls in a physical room.
- Decay
- The reverberation time, i.e. the time it takes for the reverb to go silent after sound has passed through it.
- Dampen
- Adds damping to high frequencies so that they decay faster than low frequencies.
- Size
- Adjust the size of the virtual room that reverb simulates. Ranges from closet to church. While the Size knob allows incoming modulations, it is not advisable to modulate it with anything other than a Macro, since it will add crackling artifacts to the sound whenever it is moved.
- Width
- Adjusts the stereo width of the reverb. At 100% the left and right channels are completely uncorrelated in the wet sound.
- Early
- Adjusts the balance between early and late reflections. A higher value will give a brighter and more responsive reverb.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Reverser
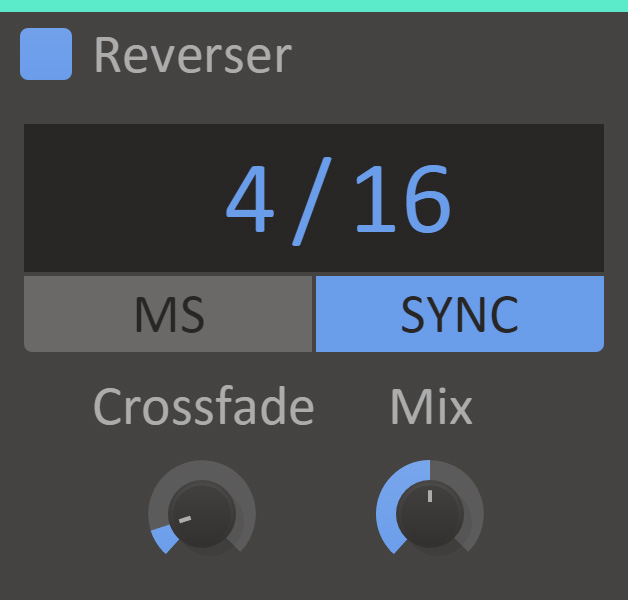 Reverser plays back delayed reversed sections of the input, mixed with the original dry sound.
Reverser plays back delayed reversed sections of the input, mixed with the original dry sound.
- Delay time
- How long sections to delay and reverse. For example, setting this to 1/4th means every beat will be played back in reverse 1/4th of a bar later.
- Sync
- When sync is enabled the delay time will be synchronized to the song tempo.
- Crossfade
- Time to ramp in/out the reversed audio to avoid pops, in percent of the reversed section length.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
Ring Mod
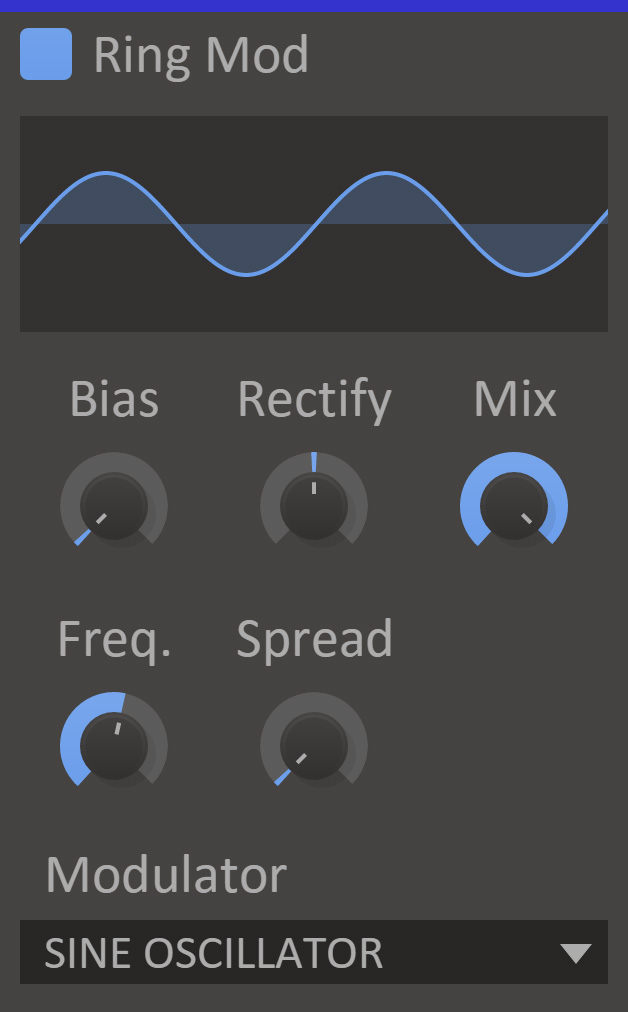 Ring Mod modulates the input with either an internal signal generator or a secondary input signal.
Ring Mod modulates the input with either an internal signal generator or a secondary input signal.
- Bias
- Amount of positive bias to add to the secondary input.
- Rectify
- Amount of positive or negative rectification to apply to the of the secondary input.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Frequency
- The base frequency of the internal oscillator or filter cutoff for the internal noise generator.
- Spread
- Shifts the frequency of the internal generator slightly for left and right channels to achieve a stereo effect.
Stereo
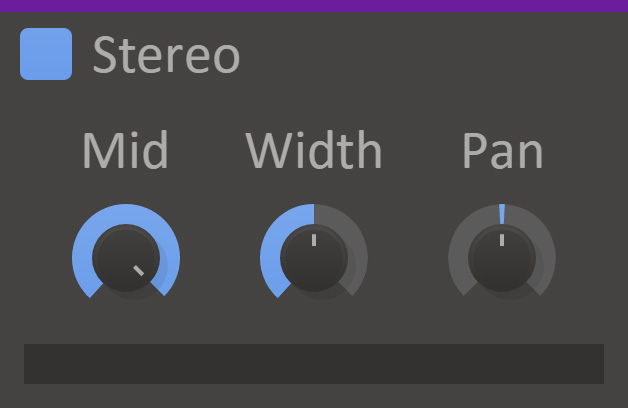 Stereo can adjust the stereo width and panning. It also displays the current balance and channel correlation visually.
Stereo can adjust the stereo width and panning. It also displays the current balance and channel correlation visually.
- Mid
- Adjusts the volume of the mono part of the signal.
- Width
- Adjusts the volume of the stereo part of the signal. The input audio must have at least a little stereo information for this knob to do anything.
- Pan
- Pans the signal to the left or right.
- Stereo Meter
- Displays the current balance and channel correlation. When the meter moves into the red area the correlation is less than zero, which can cause problems with mono compatibility.
Shaper
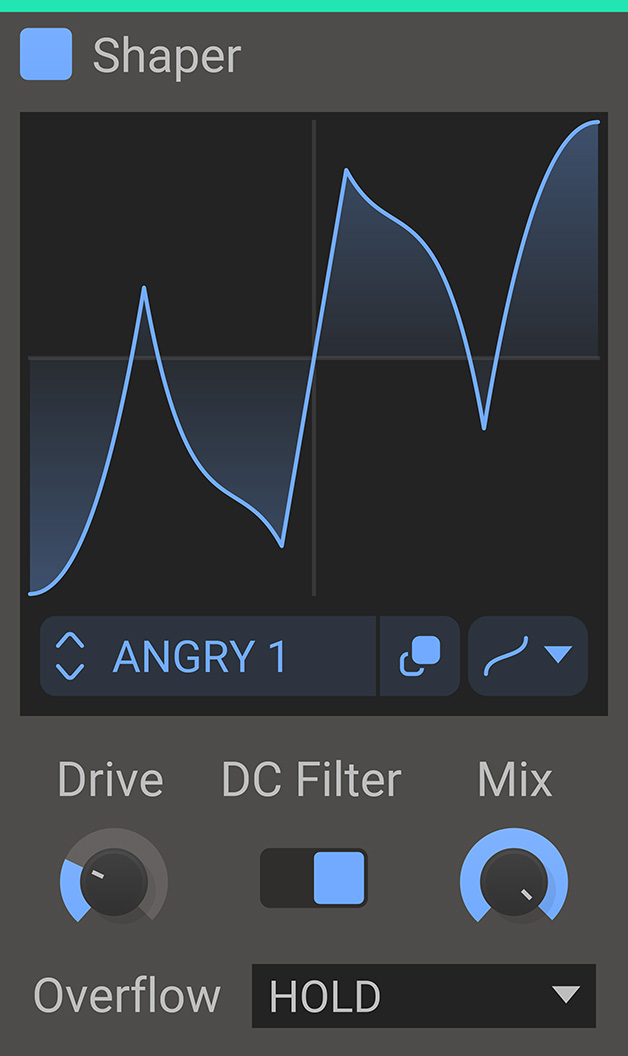 Shaper remaps the incoming audio level according to a customizable graph for bespoke distortion.
Shaper remaps the incoming audio level according to a customizable graph for bespoke distortion.
- Drive
- The drive setting will boost the input signal, causing a heavier distortion.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Overflow
- Select what happens beyond the edges of the wave shape curve. Repeat the wave, hold the edge value, or repeat with mirroring.
- DC Filter
- Enables a DC filter that fixes any DC offset introduced by the distortion.
Tape Stop
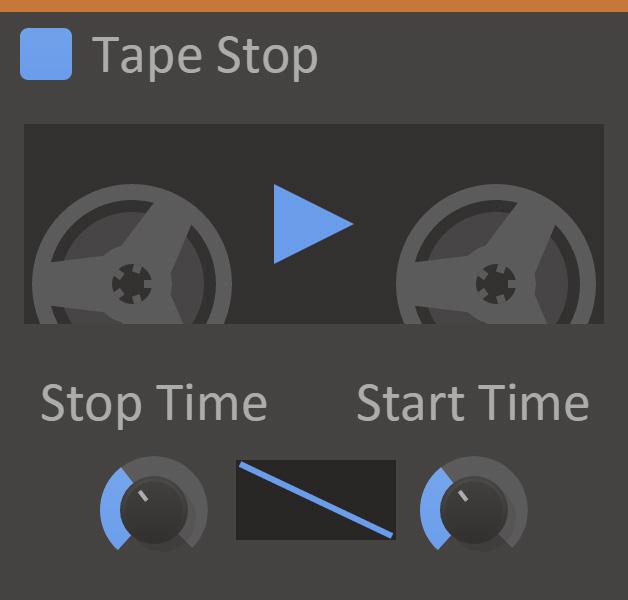 Tape Stop simulates the sound of slowly stopping and starting a playing tape.
Tape Stop simulates the sound of slowly stopping and starting a playing tape.
- Play
- The current state of the tape motor.
- Stop Time
- Time until the tape motor reaches full stop when stopping.
- Start Time
- Time until the tape motor reaches full speed when starting.
- Curve
- The speed curve of the tape motor starting/stopping.
Trance Gate
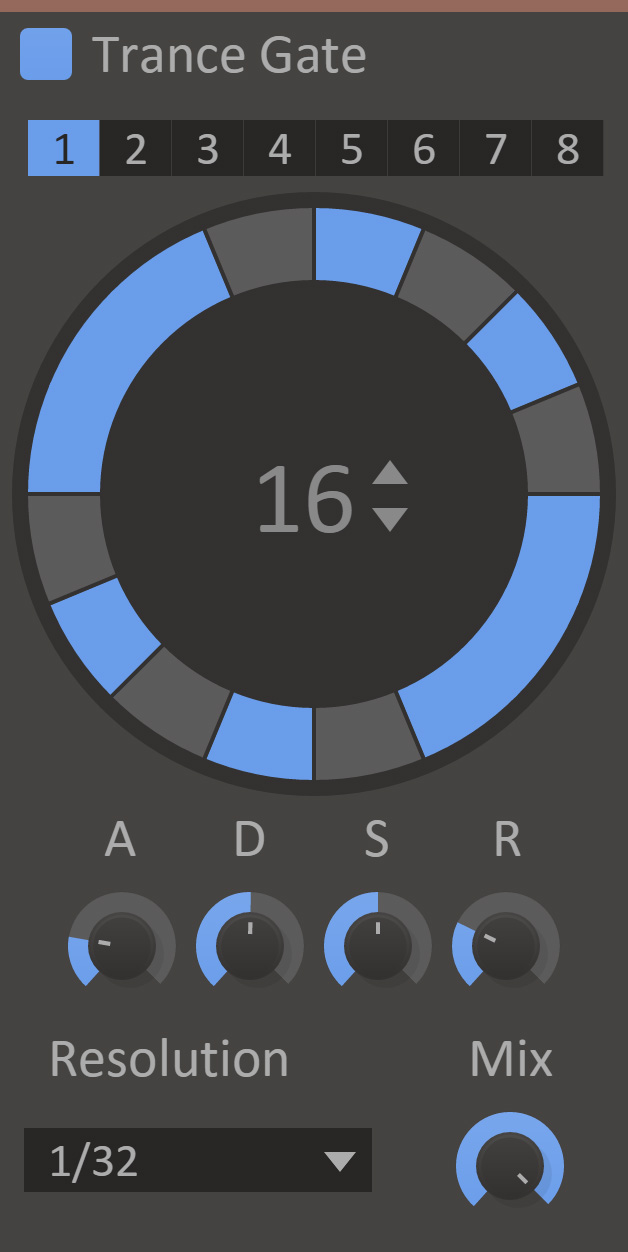 Trance Gate will modulate the volume of your audio based on a programmable rhythmic sequence.
Trance Gate will modulate the volume of your audio based on a programmable rhythmic sequence.
- Pattern Select
- Switches between the eight different pattern slots.
- Pattern Editor
- Edits the current pattern. Click to toggle steps on or off, click and drag to tie steps together.
- Length
- The length of the current pattern.
- Attack
- Attack time for the amplitude ADSR envelope.
- Decay
- Decay time for the amplitude ADSR envelope.
- Sustain
- Sustain level for the amplitude ADSR envelope.
- Release
- Release time for the amplitude ADSR envelope.
- Mix
- The dry/wet mix of this effect. A lower value will let some of the unmodified signal through.
- Resolution
- Length of one step in the sequencer.
Transient Shaper
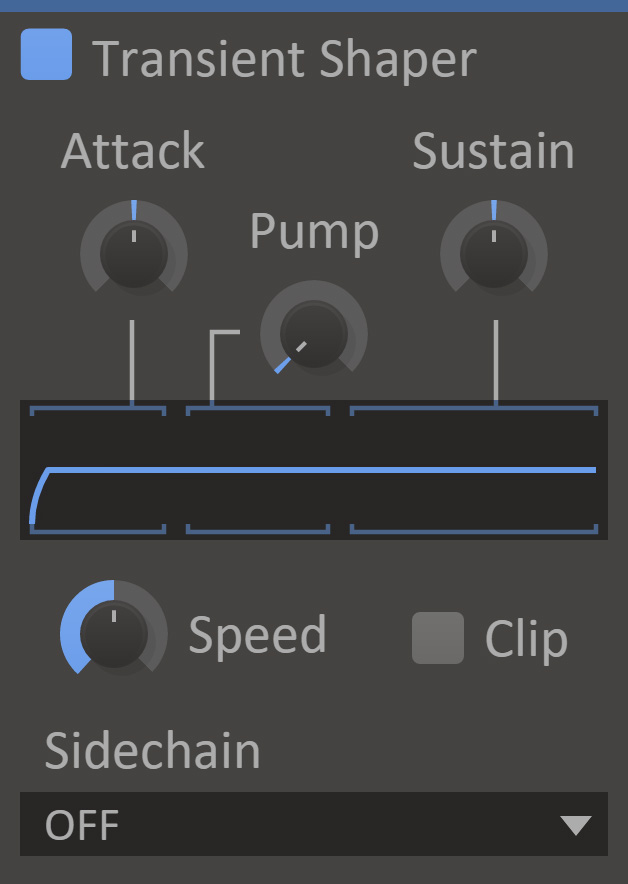 Transient Shaper adjusts the dynamics of a sound, with a focus on the initial hit; the transient.
Transient Shaper adjusts the dynamics of a sound, with a focus on the initial hit; the transient.
- Attack
- The amount of amplification or attenuation of the transient.
- Pump
- The amount of attenuation directly after the transient, emphasizing the transient without increasing the level.
- Sustain
- The amount of amplification or attenuation of the sustained sound.
- Speed
- Higher values results in snappier transient modification, and lower values result in smoother curves.
- Clip
- When enabled, the output signal is clipped to 0dB.
- Sidechain
- When enabled transients are detected based on a secondary input, but the effect is applied to the main input. (See our guide to setting up sidechains in all DAWs here)